Page 79 - Application Notebook - Solution for Food Safety
P. 79
Application No.C140
News
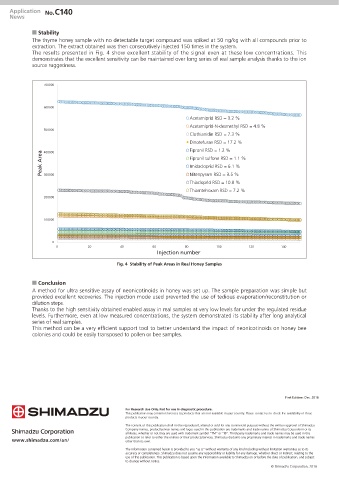
Q Stability
The thyme honey sample with no detectable target compound was spiked at 50 ng/kg with all compounds prior to
extraction. The extract obtained was then consecutively injected 150 times in the system.
The results presented in Fig. 4 show excellent stability of the signal even at these low concentrations. This
demonstrates that the excellent sensitivity can be maintained over long series of real sample analysis thanks to the ion
source ruggedness.
700000
600000
Acetamiprid RSD = 3.2 %
Acetamiprid-N-desmethyl RSD = 4.8 %
500000
Clothianidin RSD = 7.3 %
Dinotefuran RSD = 17.2 %
Fipronil RSD = 1.2 %
Peak Area Fipronil sulfone RSD = 1.1 %
400000
Imidacloprid RSD = 6.1 %
Nitenpyram RSD = 3.5 %
300000
Thiacloprid RSD = 10.8 %
Thiamtehoxam RSD = 7.2 %
200000
100000
0
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140
Injection number
Fig. 4 Stability of Peak Areas in Real Honey Samples
Q Conclusion
A method for ultra sensitive assay of neonicotinoids in honey was set up. The sample preparation was simple but
provided excellent recoveries. The injection mode used prevented the use of tedious evaporation/reconstitution or
dilution steps.
Thanks to the high sensitivity obtained enabled assay in real samples at very low levels far under the regulated residue
levels. Furthermore, even at low measured concentrations, the system demonstrated its stability after long analytical
series of real samples.
This method can be a very efficient support tool to better understand the impact of neonicotinoids on honey bee
colonies and could be easily transposed to pollen or bee samples.
First Edition: Dec. 2016
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedure.
This publication may contain references to products that are not available in your country. Please contact us to check the availability of these
products in your country.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu.
Company names, product/service names and logos used in this publication are trademarks and trade names of Shimadzu Corporation or its
affiliates, whether or not they are used with trademark symbol “TM” or “®”. Third-party trademarks and trade names may be used in this
publication to refer to either the entities or their products/services. Shimadzu disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names
www.shimadzu.com/an/ other than its own.
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject
to change without notice.
© Shimadzu Corporation, 2016