Page 65 - Application Notebook - Solution for Food Safety
P. 65
Application No.L509
News
Q Analysis of Quinolones in Meat Q Similarity Calculation Using UV Spectral Library
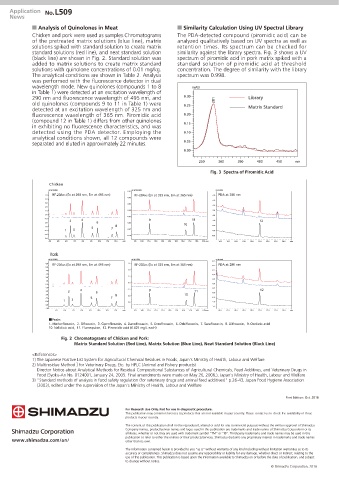
Chicken and pork were used as samples.Chromatograms The PDA-detected compound (piromidic acid) can be
of the pretreated matrix solutions (blue line), matrix analyzed qualitatively based on UV spectra as well as
solutions spiked with standard solution to create matrix retention times. Its spectrum can be checked for
standard solutions (red line), and neat standard solution similarity against the library spectra. Fig. 3 shows a UV
(black line) are shown in Fig. 2. Standard solution was spectrum of piromidic acid in pork matrix spiked with a
added to matrix solutions to create matrix standard standard solution of piromidic acid at threshold
solutions with quinolone concentrations of 0.01 mg/kg. concentration. The degree of similarity with the library
The analytical conditions are shown in Table 2. Analysis spectrum was 0.998.
was performed with the fluorescence detector in dual
wavelength mode. New quinolones (compounds 1 to 8 mAU
in Table 1) were detected at an excitation wavelength of
290 nm and fluorescence wavelength of 495 nm, and 0.30 281 Library
old quinolones (compounds 9 to 11 in Table 1) were 0.25 Matrix Standard
detected at an excitation wavelength of 325 nm and
fluorescence wavelength of 365 nm. Piromidic acid 0.20
(compound 12 in Table 1) differs from other quinolones 0.15
in exhibiting no fluorescence characteristics, and was
detected using the PDA detector. Employing the 0.10
analytical conditions shown, all 12 compounds were 0.05
separated and eluted in approximately 22 minutes.
0.00
250 300 350 400 450 nm
Fig. 3 Spectra of Piromidic Acid
Chicken
uV (x10,000) 0.07 uV (x100,000) uV (x100)
RF-20AXS (Ex at 290 nm, Em at 495 nm) PDA at 280 nm
5.0 RF-20AXS (Ex at 325 nm, Em at 365 nm) -2.0
0.05
4.0
-3.0
3.0
0.03
-4.0
2.0
1.0 0.00 -5.0
0.0 -6.0
-0.03
-1.0 4 9 11
2 -7.0 12
-2.0 6 -0.05 10
-3.0 5 7 8 -8.0
1 3 -0.07
-4.0 -9.0
-5.0
-0.10 -10.0
-6.0
4.0 5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0 12.0 min 9.0 10.0 11.0 12.0 13.0 14.0 15.0 16.0 17.0 18.0 19.0 min 16.0 17.0 18.0 19.0 20.0 21.0 22.0 23.0 24.0 min
Pork
uV (x10,000) uV (x1,000) uV (x1,000)
-0.1
6.0 7.5 PDA at 280 nm
RF-20AXS (Ex at 290 nm, Em at 495 nm) RF-20AXS (Ex at 325 nm, Em at 365 nm)
5.0 -0.2
4.0 5.0 -0.3
3.0 -0.4
2.5
2.0
-0.5
1.0
0.0 -0.6
0.0
-1.0 4 -2.5 9 -0.7 12
-2.0 2 6 11 -0.8
-3.0 8 -5.0 10
-4.0 3 5 7 -0.9
-5.0 1 -7.5 -1.0
-6.0
-1.1
-7.0
5.0 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 10.0 11.0 12.0 min 9.0 10.0 11.0 12.0 13.0 14.0 15.0 16.0 17.0 18.0 19.0min 16.0 17.0 18.0 19.0 20.0 21.0 22.0 23.0 24.0 min
˙Peaks
1. Marbofloxacin, 2. Ofloxacin, 3. Ciprofloxacin, 4. Danofloxacin, 5. Enrofloxacin, 6. Orbifloxacin, 7. Sarafloxacin, 8. Difloxacin, 9. Oxolinic acid
10. Nalidixic acid, 11. Flumequine, 12. Piromidic acid (0.025 mg/L each)
Fig. 2 Chromatograms of Chicken and Pork:
Matrix Standard Solution (Red Line), Matrix Solution (Blue Line), Neat Standard Solution (Black Line)
<References>
1) The Japanese Positive List System for Agricultural Chemical Residues in Foods, Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
2) Multiresidue Method ᶗfor Veterinary Drugs, Etc. by HPLC (Animal and Fishery products)
Director Notice about Analytical Methods for Residual Compositional Substances of Agricultural Chemicals, Feed Additives, and Veterinary Drugs in
Food (Syoku-An No. 0124001, January 24, 2005. Final amendments were made on May 26, 2006.), Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
3) "Standard methods of analysis in food safety regulation (for veterinary drugs and animal feed additives)" p.26-43, Japan Food Hygiene Association
(2003), edited under the supervision of the Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
First Edition: Oct. 2016
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedure.
This publication may contain references to products that are not available in your country. Please contact us to check the availability of these
products in your country.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu.
Company names, product/service names and logos used in this publication are trademarks and trade names of Shimadzu Corporation or its
affiliates, whether or not they are used with trademark symbol “TM” or “®”. Third-party trademarks and trade names may be used in this
publication to refer to either the entities or their products/services. Shimadzu disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names
www.shimadzu.com/an/ other than its own.
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject
to change without notice.
© Shimadzu Corporation, 2016