Page 62 - Application Notebook - Solution for Food Safety
P. 62
LAAN-A-LM-E075
Application Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
News Analysis of Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxin Using Triple
Quadrupole LC/MS/MS (LCMS-8050)
No.C104
The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare
(JMHLW) specified in July, 1980 that the mouse bioassy
(MBA) be used as the official method for diarrhetic 100000 PTX6 906.50 > 835.40(+)
shellfish toxin, and that the permissible exposure limit be 95000 OA 803.50 > 255.20(-) (4.00)
)
0.05 MU per gram of edible shellfish* . Shellfish in which 90000 YTX1 1141.50 > 1061.30(-) (9.00)
DTX1 817.50 > 255.20(-) (5.00)
the toxin exceeds this limit are prohibited from being sold PTX1 892.60 > 821.40(+)
at market according to the Japanese Food Sanitation Law 85000 PTX2 876.50 > 805.40(+)
Article 6, Item 2. 80000 PTX6
Due to significant technological advances since 1980, the 75000
sensitivity and accuracy obtained using the MBA method OA
are significantly inferior compared to the high-precision, 70000
high-sensitivity possible using liquid chromatography 65000
mass spectrometry analytical instrumentation, which is YTX1
currently used for this application. A complete transition 60000 DTX1
to instrumental analysis for lipophilic marine biotoxins is 55000
scheduled to be implemented by January 2015 50000
throughout the EU.
Based on this international trend, the JMHLW is currently 45000 PTX2
considering migration to an instrumental analysis assay 40000
and setting new reference values to be used with PTX1
instrumental analysis, in addition to the introduction of 35000
the Codex standard for okadaic acids (OA, Reference 1). 30000
25000
Table 1 CODEX Standard 292-2008
20000
Reference Value
15000
OA Acids Permissible ingestion limit of 0.16 mg
(OA and DTX group) OA per kg of edible shellfish 10000
5000
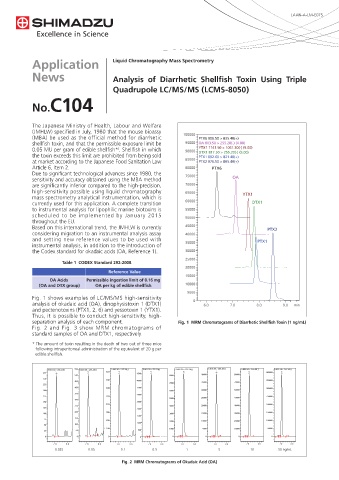
Fig. 1 shows examples of LC/MS/MS high-sensitivity 0
analysis of okadaic acid (OA), dinophysistoxin 1 (DTX1) 6.0 7.0 8.0 9.0 min
and pectenotoxins (PTX1, 2, 6) and yessotoxin 1 (YTX1).
Thus, it is possible to conduct high-sensitivity, high-
separation analysis of each component. Fig. 1 MRM Chromatograms of Diarrhetic Shellfish Toxin (1 ng/mL)
Fig. 2 and Fig. 3 show MRM chromatograms of
standard samples of OA and DTX1, respectively.
* The amount of toxin resulting in the death of two out of three mice
following intraperitoneal administration of the equivalent of 20 g per
edible shellfish.
5:803.50> 255.20(-) 550 5:803.50> 255.20(-) 5:803.50> 255.20(-) 5:803.50> 255.20(-) 5:803.50> 255.20(-) 5:803.50> 255.20(-) 5:803.50> 255.20(-) 5:803.50> 255.20(-)
0-1
275 0-1 0-1 800 0-1 4500 0-1 0-1 0-1 400000 0-1
500 8000 40000 80000
250 700
450 4000 35000 70000 350000
225 7000
400 600 3500 300000
200 6000 30000 60000
350 3000
175 500 5000 25000 50000 250000
300
150 2500
400 200000
250 4000 20000 40000
125
2000
200 300 150000
100 3000 15000 30000
1500
150
75
200 2000 10000 20000 100000
1000
50 100
100 1000 5000 10000 50000
25 50 500
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
7.0 8.0 7.0 8.0 7.0 8.0 7.0 8.0 7.0 8.0 7.0 8.0 7.0 8.0 7.0 8.0
0.025 0.05 0.1 0.5 1 5 10 50 ng/mL
Fig. 2 MRM Chromatograms of Okadaic Acid (OA)