Page 53 - Application Notebook - Solution for Food Safety
P. 53
Application No.C138
News
2
Table 2 All MRM’s Measured in the Mycotoxin Method and Corresponding Calibration Range and R Result
Ret. Time Calibration
Compound name Parent ion MRM 1 MRM 2 MRM 3 ISTD R 2
(mins) range μg/kg
1 Aflatoxin B1 [M+H] + 6.773 313 > 241 313 > 285 313 > 269 13 C Aflatoxin B1 0.1 - 10 0.9988
2 Aflatoxin B2 [M+H] + 6.621 315 > 259 315 > 287 315 > 243 13 C Aflatoxin B2 0.1 - 10 0.9995
3 Aflatoxin G1 [M+H] + 6.453 329 > 243 329 > 200 13 C Aflatoxin G1 0.1 - 10 0.9998
4 Aflatoxin G2 [M+H] + 6.219 331 > 245 331 > 285 13 C Aflatoxin G2 0.1 - 10 0.9965
5 Ochratoxin A [M+H] + 7.509 404 > 239 404 > 221 404 > 358 13 C Ochratoxin A 0.4 - 40 0.9969
6 Fumonisin B1 [M+H] + 6.811 722 > 352 722 > 334 722 > 704 13 C Aflatoxin B2 10 - 1000 0.9937
7 Fumonisin B2 [M+H] + 7.260 706 > 318 706 > 354 706 > 688 13 C Aflatoxin B2 10 - 1000 0.9998
8 Fumonisin B3 [M+H] + 7.073 706 > 318 706 > 354 706 > 688 13 C Aflatoxin B2 10 - 1000 0.9991
9 Deoxynivalenol [M+H] + 2.372 297 > 279 297 > 249 13 C Deoxynivalenol 10 - 1000 0.9992
10 Diacetoxyscirpenol [M+NH4] + 6.349 384 > 229 384 > 307 384 > 247 13 C T2 Toxin 10 - 1000 0.9994
11 T2 [M+NH4] + 7.206 484 > 185 484 > 215 484 > 245 13 C T2 Toxin 10 - 1000 0.9989
12 HT-2 [M+Na] + 6.822 447 > 345 447 > 285 13 C T2 Toxin 10 - 1000 1.0000
13 Nivalenol [M-CH3COO] - 1.684 371 > 281 371 > 311 13 C HT-2 10 - 1000 0.9991
14 Neosolaniol [M+NH4] + 3.227 400 > 215 400 > 305 400 > 185 13 C Deoxynivalenol 10 - 1000 0.9995
15 Fusarenon X [M+H] + 2.986 355 > 247 355 > 277 13 C Deoxynivalenol 10 - 1000 0.9987
16 Zearalenone [M-H] - 7.711 317 > 175 317 > 131 317 > 273 13 C T2 Toxin 10 - 1000 0.9985
17 15-Acetyldeoxynivalenol [M+H] + 4.406 339 > 261 339 > 297 13 C Deoxynivalenol 10 - 1000 1.0000
18 3-Acetyldeoxynivalenol [M+H] + 4.618 339 > 261 339 > 297 13 C Deoxynivalenol 10 - 1000 0.9986
19 13 C HT-2 [M+NH4] + 6.844 464 > 278
20 13 C T2 [M+NH4] + 7.228 508 > 322
13
21 C Aflatoxin B1 [M+H] + 6.754 330 > 301
13
22 C Aflatoxin B2 [M+H] + 6.614 332 > 303
23 13 C Aflatoxin G1 [M+H] + 6.435 346 > 212
24 13 C Aflatoxin G2 [M+H] + 6.219 348 > 259
25 13 C Ochratoxin A [M+H] + 7.516 424 > 250
Aflatoxin B1 600 Deoxynivalenol Zearalenone
y = 16.429566x - 0.255901 y = 0.589259x + 1.113599 2.5e3 y = 2.647269x + 2.134888
150
2
2
2
R = 0.99882 500 R = 0.9992016 R = 0.9984917
Fit; Linear Weighting; 1/C Fit; Linear Weighting; 1/C Fit; Linear Weighting; 1/C
125 2.0e3
Zero not forced Zero not forced Zero not forced
400
Area Ratio 100 Area Ratio 300 Area Ratio 1.5e3
75
1.0e3
200
50
100 5.0e2
25
0 0 0.0e0
0 2 4 6 8 10 0 200 400 600 800 1000 0 200 400 600 800 1000
Conc. Ratio Conc. Ratio Conc. Ratio
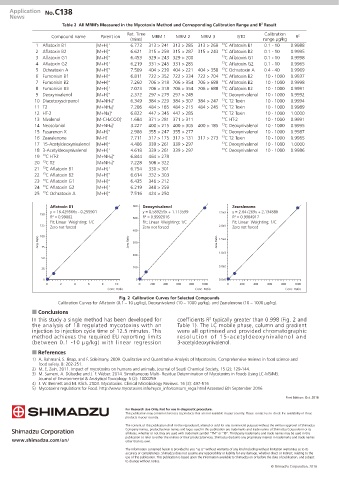
Fig. 2 Calibration Curves for Selected Compounds
Calibration Curves for Aflatoxin (0.1 – 10 μg/kg), Deoxynivalenol (10 – 1000 μg/kg), and Zearalenone (10 – 1000 μg/kg).
Q Conclusions
2
In this study a single method has been developed for coefficients R typically greater than 0.998 (Fig. 2 and
the analysis of 18 regulated mycotoxins with an Table 1). The LC mobile phase, column and gradient
injection to injection cycle time of 12.5 minutes. This were all optimised and provided chromatographic
method achieves the required EU reporting limits resolution of 15-acetyldeoxynivalenol and
(between 0.1 -10 μg/kg) with linear regression 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol.
Q References
1) A. Rahmani, S. Jinap, and F. Soleimany. 2009. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Mycotoxins. Comprehensive reviews in food science and
food safety. 8: 202-251.
2) M. E. Zain. 2011. Impact of mycotoxins on humans and animals. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society. 15 (2): 129-144.
3) M. Sameni, A. Dübecke and J. F. Weber. 2014. Simultaneous Multi- Residue Determination of Mycotoxins in Foods Using LC-MS/MS.
Journal of Environmental & Analytical Toxicology. 5 (2): 1000259
4) J. W. Bennett and M. Klich. 2003. Mycotoxins. Clinical Microbiology Reviews. 16 (3): 497-516
5) Mycotoxins regulations for Food. http://www.mycotoxins.info/myco_info/consum_regu.html Accessed 6th September 2016
First Edition: Oct. 2016
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedure.
This publication may contain references to products that are not available in your country. Please contact us to check the availability of these
products in your country.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu.
Company names, product/service names and logos used in this publication are trademarks and trade names of Shimadzu Corporation or its
affiliates, whether or not they are used with trademark symbol “TM” or “®”. Third-party trademarks and trade names may be used in this
publication to refer to either the entities or their products/services. Shimadzu disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names
www.shimadzu.com/an/ other than its own.
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject
to change without notice.
© Shimadzu Corporation, 2016