Page 22 - Application Notebook - Solution for Food Safety
P. 22
Application No.C136
News
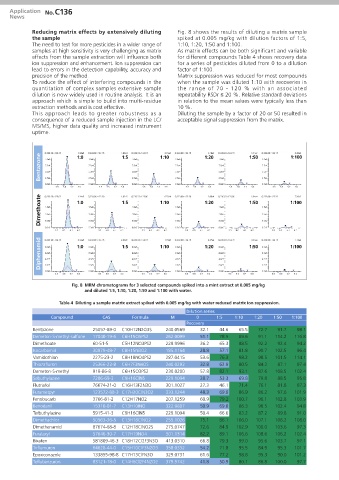
Reducing matrix effects by extensively diluting Fig. 8 shows the results of diluting a matrix sample
the sample spiked at 0.005 mg/kg with dilution factors of 1:5,
The need to test for more pesticides in a wider range of 1:10, 1:20, 1:50 and 1:100.
samples at high sensitivity is very challenging as matrix As matrix effects can be both significant and variable
effects from the sample extraction will influence both for different compounds Table 4 shows recovery data
ion suppression and enhancement. Ion suppression can for a series of pesticides diluted from 0 to a dilution
lead to errors in the detection capability, accuracy and factor of 1:100.
precision of the method. Matrix suppression was reduced for most compounds
To reduce the effect of interfering compounds in the when the sample was diluted 1:10 with recoveries in
quantitation of complex samples extensive sample the range of 70 - 120 % with an associated
dilution is now widely used in routine analysis. It is an repeatability RSDr ≤ 20 %. Relative standard deviations
approach which is simple to build into multi-residue in relation to the mean values were typically less than
extraction methods and is cost effective. 10 %.
This approach leads to greater robustness as a Diluting the sample by a factor of 20 or 50 resulted in
consequence of a reduced sample injection in the LC/ acceptable signal suppression from the matrix.
MS/MS, higher data quality and increased instrument
uptime.
Bentazone 1:0 1:5 1:10 1:20 1:50 1:100
Dimethoate 1:0 1:5 1:10 1:20 1:50 1:100
Diphenamid 1:0 1:5 1:10 1:20 1:50 1:100
Fig. 8 MRM chromatograms for 3 selected compounds spiked into a mint extract at 0.005 mg/kg
and diluted 1:5, 1:10, 1:20, 1:50 and 1:100 with water.
Table 4 Diluting a sample matrix extract spiked with 0.005 mg/kg with water reduced matrix ion suppression.
Dilution series
Compound CAS Formula M 0 1:5 1:10 1:20 1:50 1:100
Recovery
Bentazone 25057-89-0 C10H12N2O3S 240.0569 32.1 44.6 65.5 72.7 91.7 98.1
Demeton-S-methyl-sulfone 17040-19-6 C6H15O5PS2 262.0099 51.1 78.5 89.6 91.1 114.2 116.8
Dimethoate 60-51-5 C5H12NO3PS2 228.9996 36.2 65.3 88.5 92.2 92.4 94.2
Isocarbamid 30979-48-7 C8H15N3O2 185.1164 28.8 57.1 81.8 98.7 102.5 96.4
Vamidothion 2275-23-2 C8H18NO4PS2 287.0415 53.6 76.3 98.2 98.5 101.5 114.1
Thiazafluron 25366-23-8 C6H7F3N4OS 240.0293 32.8 62.9 80.5 84.2 87.1 97.4
Demeton-S-methyl 919-86-8 C6H15O3PS2 230.0200 57.8 82.1 93.1 87.6 108.5 102.4
Sebuthylazine 7286-69-3 C9H16ClN5 229.1094 28.7 53.3 69.8 79.8 88.5 95.8
Flutriafol 76674-21-0 C16H13F2N3O 301.1027 27.3 46.1 71.4 76.1 81.8 87.3
Furametpyr 123572-88-3 C17H20ClN3O2 333.1244 48.3 69.8 86.9 86.2 97.6 101.9
Fenobucarb 3766-81-2 C12H17NO2 207.1259 60.9 79.2 100.7 96.1 102.8 103.9
Benodanil 15310-01-7 C13H10INO 322.9807 50.9 69.8 86.3 96.5 102.4 94.8
Terbuthylazine 5915-41-3 C9H16ClN5 229.1094 50.4 66.6 83.2 87.2 89.8 91.0
Dimethachlor 50563-36-5 C13H18ClNO2 255.1026 75.1 86.1 106.0 107.1 106.2 108.0
Dimethenamid 87674-68-8 C12H18ClNO2S 275.0747 72.6 84.9 102.9 100.0 103.6 97.3
Furalaxyl 57646-30-7 C17H19NO4 301.1314 82.2 89.1 106.6 108.6 106.2 102.4
Bixafen 581809-46-3 C18H12Cl2F3N3O 413.0310 66.8 79.3 99.0 95.6 103.7 97.1
Triflumuron 64628-44-0 C15H10ClF3N2O3 358.0332 54.2 71.8 95.5 84.9 95.3 101.7
Epoxiconazole 133855-98-8 C17H13ClFN3O 329.0731 61.6 77.2 98.8 95.3 90.0 101.2
Teflubenzuron 83121-18-0 C14H6Cl2F4N2O2 379.9742 41.8 50.9 80.1 86.8 100.0 97.7