Page 27 - Application Notebook - Solution for Food Safety
P. 27
Application No. C154
News
Method performance
To minimize the possibility of false positive and false
negative reporting LC-MS/MS methods were
Compound Name Ethirimol developed with a high number of MRM transitions for
Formula C11H19N3O
CAS 23947-60-6 each pesticide. The performance of this approach was
RT 7.02mins compared with a conventional MRM method
monitoring 2 transitions for each pesticide.
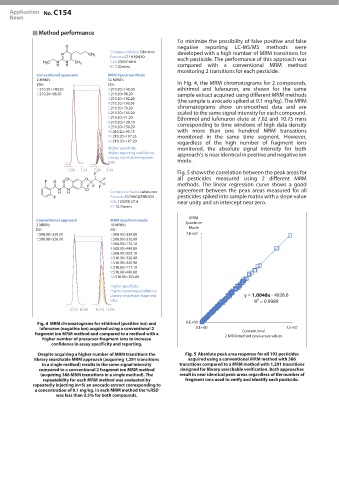
Conventional approach MRM Spectrum Mode
2 MRM’s 12 MRM’s
ESI+ ESI+ In Fig. 4, the MRM chromatograms for 2 compounds,
1:210.20>140.20 1:210.20>140.20 ethirimol and lufenuron, are shown for the same
2:210.20>98.20 2:210.20>98.20 sample extract acquired using different MRM methods
3:210.20>182.20
4:210.20>193.05 (the sample is avocado spiked at 0.1 mg/kg). The MRM
5:210.20>70.20 chromatograms show un-smoothed data and are
6:210.20>165.20 scaled to the same signal intensity for each compound.
7:210.20>71.20 Ethirimol and lufenuron elute at 7.02 and 10.75 mins
8:210.20>138.10
9:210.20>150.20 corresponding to time windows of high data density
10:210.20>95.15 with more than one hundred MRM transations
11:210.20>107.25 monitored in the same time segment. However,
12:210.20>167.20 regardless of the high number of fragment ions
Higher specificity monitored, the absolute signal intensity for both
Higher reporting confidence approach’s is near identical in positive and negative ion
Library searchable fragment
data mode.
7.00 7.24 7.00 7.24
Fig. 5 shows the correlation between the peak areas for
all pesticides measured using 2 different MRM
methods. The linear regression curve shows a good
agreement between the peak areas measured for all
Compound Name Lufenuron
Formula C17H8Cl2F8N2O3 pesticides spiked into sample matrix with a slope value
CAS 103055-07-8 near unity and an intercept near zero.
RT 10.75mins
MRM
Conventional approach MRM Spectrum mode Spectrum
2 MRM’s 10 MRM’s
ESI- ESI- Mode
1:508.90>339.00 1:508.90>339.00 7.E+07
2:508.90>326.00 2:508.90>326.00
3:508.90>175.10
4:508.90>488.80
5:508.90>202.10
6:510.90>328.00
7:510.90>340.90
8:510.90>177.10
9:510.90>490.80
10:510.90>204.00
Higher specificity
Higher reporting confidence
Library searchable fragment y = 1.0048x - 4928.6
data R² = 0.9989
10.75 10.90 10.75 10.90
MRM chromatograms for ethirimol (positive ion) and 0.E+00
lufenuron (negative ion) acquired using a conventional 2 0.E+00 Conventional 7.E+07
fragment ion MRM method and compared to a method with a 2 MRM method peak areas values
higher number of precursor-fragment ions to increase
confidence in assay specificity and reporting.
Despite acquiring a higher number of MRM transitions the Absolute peak area response for all 193 pesticides
library searchable MRM approach (acquiring 1,291 transitions acquired using a conventional MRM method with 386
in a single method) results in the same signal intensity transitions compared to a MRM method with 1,291 transitions
compared to a conventional 2 fragment ion MRM method designed for library searchable verification. Both approaches
(acquiring 386 MRM transitions in a single method). The result in near identical peak areas regardless of the number of
repeatability for each MRM method was evaluated by fragment ions used to verify and identify each pesticide.
repeatedly injecting (n=5) an avocado extract corresponding to
a concentration of 0.1 mg/kg. In each MRM method the %RSD
was less than 3.5% for both compounds.