Page 31 - Application Notebook - Solution for Food Safety
P. 31
Application No. C154
News
Data Reporting
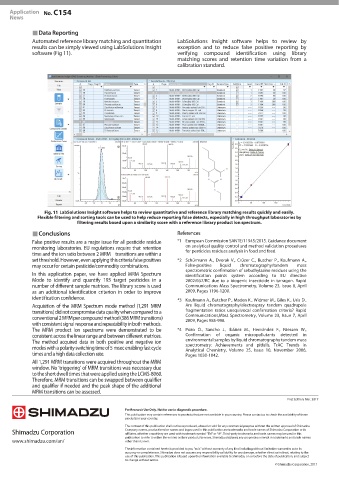
Automated reference library matching and quantitation LabSolutions Insight software helps to review by
results can be simply viewed using LabSolutions Insight exception and to reduce false positive reporting by
software (Fig 11). verifying compound identification using library
matching scores and retention time variation from a
calibration standard.
LabSolutions Insight software helps to review quantitative and reference library matching results quickly and easily.
Flexible filtering and sorting tools can be used to help reduce reporting false detects, especially in high throughput laboratories by
filtering results based upon a similarity score with a reference library product ion spectrum.
Conclusions References
False positive results are a major issue for all pesticide residue *1 European Commission SANTE/11945/2015. Guidance document
monitoring laboratories. EU regulations require that retention on analytical quality control and method validation procedures
for pesticides residues analysis in food and feed.
time and the ion ratio between 2 MRM transitions are within a
set threshold. However, even applying this criteria false positives *2 Schürmann A., Dvorak V., Crüzer C., Butcher P., Kaufmann A.,
may occur for certain pesticide/commodity combinations. False-positive liquid chromatography/tandem mass
spectrometric confirmation of sebuthylazine residues using the
In this application paper, we have applied MRM Spectrum identification points system according to EU directive
Mode to identify and quantify 193 target pesticides in a 2002/657/EC due to a biogenic insecticide in tarragon. Rapid
number of different sample matrices. The library score is used Communications Mass Spectrometry, Volume 23, Issue 8, April
as an additional identification criterion in order to improve 2009, Pages 1196-1200.
identification confidence. *3 Kaufmann A., Butcher P., Maden K., Widmer M., Giles K., Uría D..
Acquisition of the MRM Spectrum mode method (1,291 MRM Are liquid chromatography/electrospray tandem quadrupole
transitions) did not compromise data quality when compared to a fragmentation ratios unequivocal confirmation criteria? Rapid
conventional 2 MRM per compound method (386 MRM transitions) Communications,Mass Spectrometry, Volume 23, Issue 7, April
2009, Pages 985-998.
with consistent signal response and repeatability in both methods.
The MRM product ion spectrums were demonstrated to be *4 Pozo Ó., Sancho J., Ibáñez M., Hernández F., Niessen W.,
consistent across the linear range and between different matrices. Confirmation of organic micropollutants detected in
The method acquired data in both positive and negative ion environmental samples by liquid chromatography tandem mass
spectrometry: Achievements and pitfalls, TrAC Trends in
modes with a polarity switching time of 5 msec enabling fast cycle Analytical Chemistry, Volume 25, Issue 10, November 2006,
times and a high data collection rate. Pages 1030-1042.
All 1,291 MRM transitions were acquired throughout the MRM
window. No ‘triggering’ of MRM transitions was necessary due
to the short dwell times that were applied using the LCMS-8060.
Therefore, MRM transitions can be swapped between qualifier
and qualifier if needed and the peak shape of the additional
MRM transitions can be assessed.
First Edition: Mar. 2017
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedure.
This publication may contain references to products that are not available in your country. Please contact us to check the availability of these
products in your country.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu.
Company names, product/service names and logos used in this publication are trademarks and trade names of Shimadzu Corporation or its
affiliates, whether or not they are used with trademark symbol “TM” or “£”. Third-party trademarks and trade names may be used in this
publication to refer to either the entities or their products/services. Shimadzu disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names
www.shimadzu.com/an/ other than its own.
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject
to change without notice.
© Shimadzu Corporation, 2017