Page 25 - Application Notebook - PFAS Analysis
P. 25
SSI-LCMS-102
■ Method
This application news describes and demonstrates the use PFAS may be present in sampling containers and other
and performance of Shimadzu UFMS for the analysis of 25 consumables employed during the sample preparation and
PFAS (18 targets, 4 surrogates, and 3 internal standards) in analysis steps. To minimize the contribution of PFAS
drinking water. Standards were purchased from background contamination, a Shim-Pack XR-ODS 50 x 3.0
Wellington Laboratories. mm column was used as a delay column (Part No. 228-
41606-92). This column is situated before the autosampler
The Shimadzu LCMS-8045, a triple quadrupole mass and causes a delay in the elution of PFAS present in the
spectrometer, was used in this study. MRM transitions background, allowing for their separation from the target
were optimized using Flow Injection Analysis (FiA) for all analytes in the samples. Mobile Phase A consisted of 20
compounds. Source parameters were optimized to reduce mM ammonium acetate and Mobile Phase B consisted of
in-source fragmentation for GenX. No compounds LCMS grade methanol with no additives. Compounds,
suffered a loss in signal intensity because of the re- including PFHxS and PFOS isomers, were separated using a
optimized conditions for GenX. Shim-pack™ Velox, 2.1 mm ID × 150 mm, 2.7 μm particle
size (Shimadzu Part No. 227-32009-04).
Figures 1 and 2 compare the chromatograms for all PFAS
in the original EPA Method 537 as well as the updated EPA
Method 537.1.
A detailed description of the LC/MS/MS parameters is
included in Tables 2 and 3.
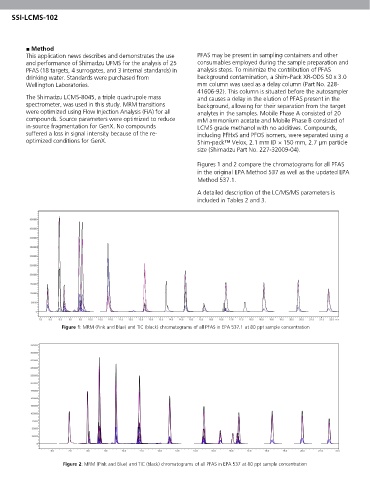
Figure 1: MRM (Pink and Blue) and TIC (black) chromatograms of all PFAS in EPA 537.1 at 80 ppt sample concentration
Figure 2: MRM (Pink and Blue) and TIC (black) chromatograms of all PFAS in EPA 537 at 80 ppt sample concentration