Page 26 - LC-SFC_Pharma_Brochure
P. 26
3-2. Converting a Method for Sulfa Drug Analysis for General Use
3-2. Converting a Method for Sulfa Drug Analysis for General Use
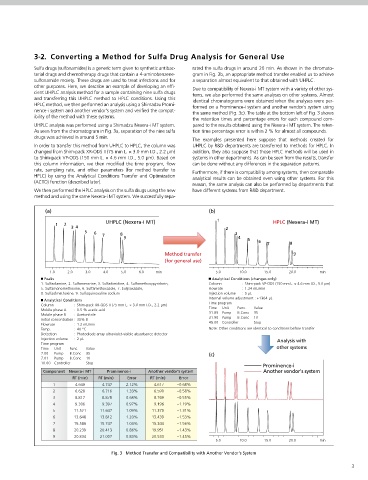
Sulfa drugs (sulfonamides) is a generic term given to synthetic antibac- rated the sulfa drugs in around 20 min. As shown in the chromato-
terial drugs and chemotherapy drugs that contain a 4-aminobenzene- gram in Fig. 3b, an appropriate method transfer enabled us to achieve
sulfonamide moiety. These drugs are used to treat infections and for a separation almost equivalent to that obtained with UHPLC.
other purposes. Here, we describe an example of developing an effi- Due to compatibility of Nexera-i MT system with a variety of other sys-
cient UHPLC analysis method for a sample containing nine sulfa drugs tems, we also performed the same analyses on other systems. Almost
and transferring this UHPLC method to HPLC conditions. Using this identical chromatograms were obtained when the analyses were per-
HPLC method, we then performed an analysis using a Shimadzu Promi- formed on a Prominence-i system and another vendor's system using
nence-i system and another vendor's system and verified the compat- the same method (Fig. 3c). The table at the bottom left of Fig. 3 shows
ibility of the method with these systems.
the retention times and percentage errors for each compound com-
UHPLC analysis was performed using a Shimadzu Nexera-i MT system. pared to the results obtained using the Nexera-i MT system. The reten-
As seen from the chromatogram in Fig. 3a, separation of the nine sulfa tion time percentage error is within 2 % for almost all compounds.
drugs was achieved in around 5 min.
The examples presented here suppose that methods created for
In order to transfer this method from UHPLC to HPLC, the column was UHPLC by R&D departments are transferred to methods for HPLC. In
changed from Shim-pack XR-ODS II (75 mm L. × 3.0 mm I.D., 2.2 µm) addition, they also suppose that those HPLC methods will be used in
to Shim-pack VP-ODS (150 mm L. × 4.6 mm I.D., 5.0 µm). Based on systems in other departments. As can be seen from the results, transfer
this column information, we then modified the time program, flow can be done without any differences in the separation patterns.
rate, sampling rate, and other parameters (for method transfer to Furthermore, if there is compatibility among systems, then comparable
HPLC) by using the Analytical Conditions Transfer and Optimization analytical results can be obtained even using other systems. For this
(ACTO) function (described later).
reason, the same analysis can also be performed by departments that
We then performed the HPLC analysis on the sulfa drugs using the new have different systems from R&D department.
method and using the same Nexera-i MT system. We successfully sepa-
(a) (b)
UHPLC (Nexera-i MT) 1 HPLC (Nexera-i MT)
1 2
3 4 2
5 6 3
7 8
9 4 5
6
7 8
Method transfer 9
(for general use)
1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 5.0 6.0 min 5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 min
ů Peaks ů Analytical Conditions (changes only)
1. Sulfadiamine, 2. Sulfamerazine, 3. Sulfadimidine, 4. Sulfamethoxypyridazin, Column : Shim-pack VP-ODS (150 mm L. × 4.6 mm I.D., 5.0 µm)
5. Sulfamonomethoxine, 6. Sulfamethoxazole, 7. Sulÿsoxazole, Flowrate : 1.24 mL/min
8. Sulfadimethoxine, 9. Sulfaquinoxaline sodium Injection volume : 5 µL
ů Analytical Conditions Internal volume adjustment : +1364 µL
Column : Shim-pack XR-ODS II (75 mm L. × 3.0 mm I.D., 2.2 µm) Time program
Mobile phase A : 0.5 % acetic acid Time Unit Func. Value
Mobile phase B : Acetonitrile 31.85 Pump B.Conc 35
Initial concentration : 35% B 31.90 Pump B.Conc 10
Flowrate : 1.2 mL/min 45.00 Controller Stop
Temp. : 40 °C Note: Other conditions are identical to conditions before transfer
Detection : Photodiode array ultraviolet-visible absorbance detector
Injection volume : 2 µL Analysis with
Time program
Time Unit Func. Value other systems
7.00 Pump B.Conc 35 (c)
7.01 Pump B.Conc 10
10.00 Controller Stop
Prominence-i
Component Nexera-i MT Prominence-i Another vendor's system Another vendor's system
RT (min) RT (min) Error RT (min) Error
1 4.649 4.747 2.12% 4.617 −0.68%
2 6.628 6.716 1.33% 6.590 −0.58%
3 8.817 8.878 0.68% 8.769 −0.55%
4 9.306 9.397 0.97% 9.196 −1.19%
5 11.521 11.647 1.09% 11.370 −1.31%
6 13.648 13.812 1.20% 13.439 −1.53%
7 15.586 15.747 1.03% 15.344 −1.56%
8 20.239 20.413 0.86% 19.951 −1.43%
9 20.834 21.007 0.83% 20.533 −1.45%
5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 min
Fig. 3 Method Transfer and Compatibility with Another Vendor's System
3