Page 17 - LC-SFC_Pharma_Brochure
P. 17
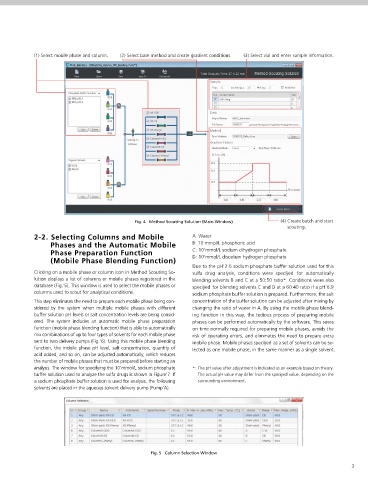
(1) Select mobile phase and column. (2) Select base method and create gradient conditions. (3) Select vial and enter sample information.
Fig. 4 Method Scouting Solution (Main Window) (4) Create batch and start
s couting.
2-2. Selecting Columns and Mobile A: Water
Phases and the Automatic Mobile B: 10 mmol/L phosphoric acid
Phase Preparation Function C: 10‘mmol/L sodium dihydrogen phosphate
(Mobile Phase Blending Function) D: 10‘mmol/L disodium hydrogen phosphate
Due to the pH‘2.6 sodium phosphate buffer solution used for this
Clicking on a mobile phase or column icon in Method Scouting So- sulfa drug analysis, conditions were speciÿed for automatically
lution displays a list of columns or mobile phases registered in the blending solvents B and C at a 50:50 ratio*. Conditions were also
database (Fig.‘5). This window is used to select the mobile phases or speciÿed for blending solvents C and D at a 60:40 ratio if a pH‘6.9
columns used to scout for analytical conditions. sodium phosphate buffer solution is prepared. Furthermore, the salt
This step eliminates the need to prepare each mobile phase being con- concentration of the buffer solution can be adjusted after mixing by
sidered by the system when multiple mobile phases with different changing the ratio of water in A. By using the mobile phase blend-
buffer solution pH levels or salt concentration levels are being consid- ing function in this way, the tedious process of preparing mobile
ered. The system includes an automatic mobile phase preparation phases can be performed automatically by the software. This saves
function (mobile phase blending function) that is able to automatically on time normally required for preparing mobile phases, avoids the
mix combinations of up to four types of solvents for each mobile phase risk of operating errors, and eliminates the need to prepare extra
sent to two delivery pumps (Fig.‘6). Using this mobile phase blending mobile phase. Mobile phases speciÿed as a set of solvents can be se-
function, the mobile phase pH level, salt concentration, quantity of lected as one mobile phase, in the same manner as a single solvent.
acid added, and so on, can be adjusted automatically, which reduces
the number of mobile phases that must be prepared before starting an
analysis. The window for specifying the 10‘mmol/L sodium phosphate *: The pH value after adjustment is indicated as an example based on theory.
buffer solution used to analyze the sulfa drugs is shown in Figure‘7. If The actual pH value may differ from the speciÿed value, depending on the
a sodium phosphate buffer solution is used for analysis, the following surrounding environment.
solvents are placed in the aqueous solvent delivery pump (Pump‘A).
Fig. 5 Column Selection Window
3