Page 9 - LifeScience Solutions for Stem Cell Analysis
P. 9
A Micro-fluidic Approach using
a Super-functional Liver Chip
Micro-fluidic
Data
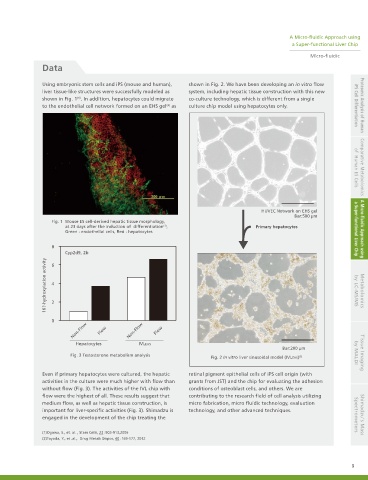
Using embryonic stem cells and iPS (mouse and human), shown in Fig. 2. We have been developing an in vitro flow
liver tissue-like structures were successfully modeled as system, including hepatic tissue construction with this new
(1)
shown in Fig. 1 . In addition, hepatocytes could migrate co-culture technology, which is different from a single
(2)
to the endothelial cell network formed on an EHS gel as culture chip model using hepatocytes only. iPS Cell Differentiation Proteomic Analysis of Human
HUVEC Network on EHS gel of Human ES Cells Comparative Metabolomics
Bar:500 µm
Fig. 1 Mouse ES cell-derived hepatic tissue morphology,
at 23 days after the induction of differentiation , Primary hepatocytes
(1)
Green : endothelial cells, Red : hepatocytes a Super-functional Liver Chip A Micro-fluidic Approach using
8
Cyp2d9, 2b
16?-hydroxylation activity 4 2 by LC-MS/MS Metabolomics
6
0
Non-Flow Flow Non-Flow Flow
Hepatocytes IVLEHS
Bar:200 µm
Fig. 3 Testosterone metabolism analysis by MALDI Tissue Imaging
Fig. 2 In vitro liver sinusoidal model (IVLEHS) (2)
Even if primary hepatocytes were cultured, the hepatic retinal pigment epithelial cells of iPS cell origin (with
activities in the culture were much higher with flow than grants from JST) and the chip for evaluating the adhesion
without flow (Fig. 3). The activities of the IVL chip with conditions of osteoblast cells, and others. We are
flow were the highest of all. These results suggest that contributing to the research field of cell analysis utilizing
medium flow, as well as hepatic tissue construction, is micro fabrication, micro fluidic technology, evaluation
important for liver-specific activities (Fig. 3). Shimadzu is technology, and other advanced techniques.
engaged in the development of the chip treating the Spectrometers Shimadzu’s Mass
(1)Ogawa, S., et. al. , Stem Cells, 23 :903-913,2005
(2)Toyoda, Y., et .al., Drug Metab Dispos, 40 :169-177, 2012
9