Page 18 - Application Notebook - PFAS Analysis
P. 18
Application No. C184
News
Since PFAS is ubiquitously present on laboratory Q 398.90>80.10 (-) RT=9.654 5.71e4
equipment such as tubing and HPLC systems, it is 100.00
impossible to completely eliminate PFAS from LC
mobile phases even if LCMS-grade reagent solvents
have been used. This necessitates the use of a solvent
delay column for high-sensitivity analysis. A small C18
column that have higher retention of PFAS than the %
analytical column is placed directly upstream of
autosampler to trap all PFAS contained in the mobile
phase. During chromatographic elution, the analytical
column gives sample-derived PFAS peaks first,
separated from secondary peaks derived from mobile
phase contamination trapped on the delay column. 0.00
9.4 9.6 9.8 10.0
RT
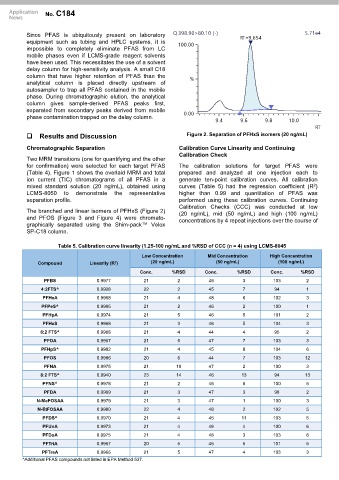
Results and Discussion Figure 2. Separation of PFHxS isomers (20 ng/mL)
Chromatographic Separation Calibration Curve Linearity and Continuing
Calibration Check
Two MRM transitions (one for quantifying and the other
for confirmation) were selected for each target PFAS The calibration solutions for target PFAS were
(Table 4). Figure 1 shows the overlaid MRM and total prepared and analyzed at one injection each to
ion current (TIC) chromatograms of all PFAS in a generate ten-point calibration curves. All calibration
2
mixed standard solution (20 ng/mL), obtained using curves (Table 5) had the regression coefficient (R )
LCMS-8050 to demonstrate the representative higher than 0.99 and quantitation of PFAS was
separation profile. performed using these calibration curves. Continuing
Calibration Checks (CCC) was conducted at low
The branched and linear isomers of PFHxS (Figure 2) (20 ng/mL), mid (50 ng/mL) and high (100 ng/mL)
and PFOS (Figure 3 and Figure 4) were chromato- concentrations by 4 repeat injections over the course of
graphically separated using the Shim-pack™ Velox
SP-C18 column.
Table 5. Calibration curve linearity (1.25-100 ng/mL and %RSD of CCC (n = 4) using LCMS-8045
Low Concentration Mid Concentration High Concentration
2
Compound Linearity (R ) (20 ng/mL) (50 ng/mL) (100 ng/mL)
Conc. %RSD Conc. %RSD Conc. %RSD
PFBS 0.9977 21 2 46 3 103 2
4:2FTS^ 0.9928 22 2 45 7 94 1
PFHxA 0.9968 21 4 48 6 102 3
PFPeS^ 0.9985 21 2 46 2 100 1
PFHpA 0.9974 21 5 46 5 101 2
PFHxS 0.9968 21 3 46 5 104 3
6:2 FTS^ 0.9968 21 4 44 4 95 2
PFOA 0.9967 21 5 47 7 103 3
PFHpS^ 0.9982 21 4 45 8 104 6
PFOS 0.9986 20 6 44 7 103 12
PFNA 0.9975 21 10 47 2 100 3
8:2 FTS^ 0.9940 23 14 46 13 94 13
PFNS^ 0.9978 21 2 46 6 100 5
PFDA 0.9969 21 3 47 3 98 2
N-MeFOSAA 0.9979 21 3 47 1 100 3
N-EtFOSAA 0.9980 22 4 48 2 102 5
PFDS^ 0.9970 21 4 45 11 103 5
PFUnA 0.9973 21 4 48 4 100 6
PFDoA 0.9975 21 4 48 3 103 6
PFTriA 0.9967 20 5 45 5 101 5
PFTreA 0.9966 21 5 47 4 103 3
^Additional PFAS compounds not listed in EPA Method 537.