Page 63 - LC-SFC_Pharma_Brochure
P. 63
mV
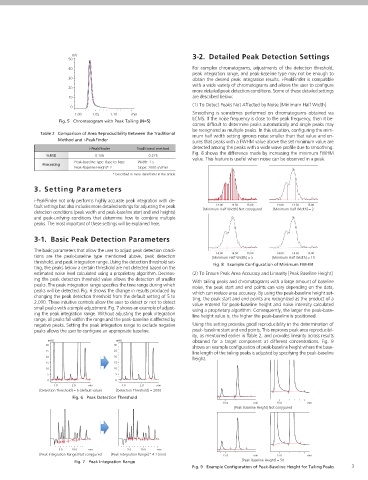
mAU mV 50 3-2. Detailed Peak Detection Settings
2.0
Main peak Impurity peak integration range, and peak-baseline type may not be enough to
[Detection Threshold] = 10 4 40 For complex chromatograms, adjustments of the detection threshold,
1.5 3 30 obtain the desired peak integration results. i-PeakFinder is compatible
20 with a wide variety of chromatograms and allows the user to configure
2
1.0 more detailed peak detection conditions. Some of these detailed settings
10 are described below:
1
0.5 0 (1) To Detect Peaks Not Affected by Noise [Minimum Half Width]
0 1.00 1.05 1.10 min Smoothing is sometimes performed on chromatograms obtained via
LCMS. If the noise frequency is close to the peak frequency, then it be-
0.0 Fig. 5 Chromatogram with Peak Tailing (N=5)
12.5 15.0 17.5 min comes difficult to determine peaks automatically and single peaks may
17.5 20.0 min [Baseline Type] Not conÿgured Table 2 Comparison of Area Reproducibility Between the Traditional be recognized as multiple peaks. In this situation, configuring the mini-
Normal shoulder peaks can be detected with no special parameter adjustment mV mum half width setting ignores noise smaller than that value and en-
Method and i-PeakFinder sures that peaks with a FWHM value above the set minimum value are
mAU 4
2.0 i-PeakFinder Traditional method detected among the peaks with a wide wave profile due to smoothing.
[Detection Threshold] = 10 Main peak Impurity %RSD 0.106 0.275 Fig. 8 shows the difference made by increasing the minimum FWHM
[Detection Threshold of 3 value. This feature is useful when noise can be observed in a peak.
1.5 Unseparated Small Peak] = 0.3 Processing Peak-baseline Type: Base to Base Width: 1 s
2 Peak-Baseline Height* 2 Slope: 2000 uV/min
* Described in more detail later in the article
1.0 1
3. Setting Parameters
3. Setting Parameters
0
0.5
i-PeakFinder not only performs highly accurate peak integration with de-
12.5 15.0 17.5 min 14.00 14.50 15.00 14.00 14.50 15.00
0.0 fault settings but also includes more detailed settings for adjusting the peak
[Baseline Type] Vertical Division [Minimum Half Width] Not conÿgured [Minimum Half Width] = 2
detection conditions (peak width and peak-baseline start and end heights)
mV
17.5 20.0 min and peak-unifying conditions that determine how to combine multiple
Even very small shoulder peaks can be detected with additional parameter adjustments. 4 peaks. The most important of these settings will be explained here.
Main peak Impurity
Fig. 2 Examples of Shoulder Peak Detection 3 3-1. Basic Peak Detection Parameters
2
2-2. Simple Adjustment of Peak-baseline The basic parameters that allow the user to adjust peak detection condi- 14.00 14.50 15.00 14.00 14.50 15.00
Processing 1 tions are the peak-baseline type mentioned above, peak detection [Minimum Half Width] = 5 [Minimum Half Width] = 10
threshold, and peak integration range. Using the detection threshold set-
ting, the peaks below a certain threshold are not detected based on the Fig. 8 Example Con guration of Minimum FWHM
Accurate detection of impurity peaks is essential for pharmaceutical 0 estimated noise level calculated using a proprietary algorithm. Decreas- (2) To Ensure Peak Area Accuracy and Linearity [Peak Baseline Height]
quality control and other applications. Impurity peaks are often fused at ing the peak detection threshold value allows the detection of smaller
the base of a major peak, and quantitative results obtained via area nor- 12.5 15.0 17.5 min peaks. The peak integration range specifies the time range during which With tailing peaks and chromatograms with a large amount of baseline
noise, the peak start and end points can vary depending on the data,
malization can vary depending on the method used for peak-baseline [Baseline Type] Base to Base peaks will be detected. Fig. 6 shows the change in results produced by which can reduce area accuracy. By using the peak-baseline height set-
processing. The method used for peak-baseline processing also differs Note: Other than peak integration range and peak-baseline processing type, all settings are at default. changing the peak detection threshold from the default setting of 5 to ting, the peak start and end points are recognized as the product of a
based on the samples and testing objectives. With traditional methods, 2,000. These intuitive controls allow the user to detect or not to detect value entered for peak-baseline height and noise intensity calculated
performing a speciÿc type of peak-baseline processing requires the user Fig. 4 Peak-baseline Processing Example small peaks with a simple adjustment. Fig. 7 shows an example of adjust- using a proprietary algorithm. Consequently, the larger the peak-base-
to include time programming or perform peak integration manually. ing the peak integration range. Without adjusting the peak integration line height value is, the higher the peak-baseline is positioned.
Table 1 Quantitative Results Obtained via Area Normalization with range, all peaks fall within the range and the peak-baseline is affected by
However, i-PeakFinder has adjustable parameters in its basic settings Different Methods of Peak-baseline Type negative peaks. Setting the peak integration range to exclude negative Using this setting provides good reproducibility in the determination of
for performing a speciÿc type of peak-baseline processing, allowing peaks allows the user to configure an appropriate baseline. peak- baseline start and end points. This improves peak area reproducibil-
the user to easily implement the optimum peak-baseline type in each Not con gured Vertical Division Base to Base ity, as mentioned earlier in Table 2, and provides linearity across results
situation. Fig. 3 shows a list of peak-baseline type in the settings Main peak 99.681 99.448 99.680 30 mAU 30 mAU obtained for a target component at different concentrations. Fig. 9
shows an example configuration of peak-baseline height where the base-
window, Fig. 4 shows the result of peak-baseline type setting of an Impurity 0.160 0.338 0.160 25 25 line length of the tailing peaks is adjusted by specifying the peak-baseline
impurity peak that is fused at the base of a major peak, and Table 1 20 20 height.
summarizes the quantitative results obtained via area normalization 2-3. Improved Peak-Baseline Positioning 15 15
with different peak-baseline type settings. Peak-baseline processing for Enhanced Reproducibility 10 10
appropriate for a particular situation can be simply performed by 5 5
changing a few basic parameters. 0 0
When a target component is separated with peak tailing or leading in 1.0 2.0 min 1.0 2.0 min
some cases, using a traditional peak integration method would result [Detection Threshold] = 5 (default value) [Detection Threshold] = 2000
in variability in the calculated peak areas depending on which point Fig. 6 Peak Detection Threshold
along the trailing and leading edge was deÿned as the peak base. 15.0 min 15.0 min
This affected the reproducibility of area results. [Peak Baseline Height] Not conÿgured
With i-PeakFinder, the user can adjust the height at which the start
and end of a peak-baseline needs to be deÿned so that peak-baseline
processing is consistent even with tailing and leading peaks.
The reproducibility of results obtained using the traditional method and
i- PeakFinder is summarized in Table 2 for the chromatogram shown in Fig.
min
10.0
5.0
5.0
10.0
min
5. In the example below, the peak area results obtained using i-PeakFinder [Peak Integration Range] Not conÿgured [Peak Integration Range] ° 4.1 (min) 15.0 min 15.0 min
exhibit superior reproducibility compared to the traditional method. [Peak Baseline Height] = 50
Fig. 3 Peak-baseline Type Settings Fig. 7 Peak Integration Range
2 Fig. 9 Example Con guration of Peak-Baseline Height for Tailing Peaks 3