Page 56 - LC-SFC_Pharma_Brochure
P. 56
4. Analysis of Standard Solutions The requirements indicated in Fig. 3 are executed via the program below.
n.drain : Needle is returned to the home position, then moved to the drain position, and then slightly
The caffeine standard stock solution will be diluted from 1/2−1/100 of lowered.
disp 600,rs : Liquid is dispensed at the set volume (600 µL) and speed (rs).
the original concentration using the pretreatment feature of the SIL- vial.n 1,105 : Needle moves to the specified rack number (1) and vial number (105).
n.strk ns : Needle is lowered by the set needle stroke (ns) value.
30AC, and each dilution level will then be injected onto the column. aspir 5.0,ss : Liquid is aspirated at set volume (post-dilution volume 100 µL / dilution factor 20 =5.0 µL) and
speed (ss).
vial.n rn,sn : Needle moves to specified rack number (rn) and vial number (sn).
n.strk ns : Needle is lowered by the set needle stroke (ns) value.
disp 100,ss : Liquid is dispensed at the set volume (100 µL) and speed (ss).
a1=2 : Defines user variable (a1=2).
4-1. Preparation Items a2=10 : Defines user variable (a2=10).
mix 3,5,45,a1,a2 : Mixing is conducted the set number of times (3 times), with specified upper air volume (5 µL),
mixing volume (45 µL), aspiration speed (a1), and discharge speed (a2).
1) Caffeine standard stock solution n.drain : Needle is returned to the home position, then moved to the drain position, and then slightly
lowered.
2) Vials for mixing (1.0 mL polypropylene vials) disp 100,rs : Liquid is dispensed at the set volume (100 µL) and speed (rs).
d.rinse : Needle moves to rinse port, and is immersed for the specified immersion time.
inj.p : Needle moves to injection port, and is lowered to bottom of injection port.
v.inj : High pressure valve is switched to injection side (flow line in which sample loop connects with
solvent delivery pump and column).
wait 1.0 : Operation waits until end of set wait time (1.0 min).
4-2. Outline of Standard Solution goto f0 : Operation shifts to the set file number (standard injection operation f0).
: Pretreatment program ends.
end
Analysis Operation Procedure Program variables (ns, rs, etc.) are defined as follows.
ns : Needle stroke set in the method
The volume of standard stock solution corresponding to the specific rs : Rinse liquid aspiration speed set in the method
ss : Sample aspiration speed set in the method
dilution ratio is aspirated from the stock solution vial, then rn : Specified rack number for batch analysis or single analysis
sn : Specified vial number for batch analysis or single analysis
dispensed into an empty vial along with the diluent. Mixing is then
conducted in this vial (matching the sample number in the sequence
table), and the specified injection volume of mixed solution is
aspirated and introduced onto the column (Fig. 2). In this example, 4-4. Standard Solution Analysis Example
one of the SIL-30AC rinse solutions (R0) was defined as the diluent.
An example of standard solution analysis is shown below. The settings
These operation steps are shown below. were performed to dilute a 500 mg/L caffeine aqueous standard stock
(1) Aspirate standard stock solution solution 100-, 50-, 20-, 10-, 5-, and 2-fold in order to obtain standard
(2) Dispense standard stock solution with diluent into empty vial solutions with final caffeine concentrations of 5 mg/L, 10 mg/L, 25
(3) Mixing mg/L, 50 mg/L, 100 mg/L and 250 mg/L, respectively. Pure water was
(4) Analysis start used as the standard stock solution diluent (rinse solution R0). The
analytical conditions are shown in Table 1, the analysis results for the
ʢ1 ʣ ʢ 2 ʣ ʢ 3 ʣ ʢ 4ʣ
various standard solutions in Fig. 4, and the calibration curve obtained
from the standard solution analysis results in Fig. 5.
To check the repeatability of the automatic dilution operations, 6
successive analyses were conducted for each automatically diluted
standard solution, and the peak area repeatability (%RSD) was
Standard stock Empty vial
Column calculated. Those results are shown in Table 2.
solution (for mixing)
(*1)
In addition, to verify the accuracy of dilution using the SIL-30AC, we
Fig. 2 Standard Solution Injection Operation Procedure
compared the peak area values obtained using standard solutions
prepared manually by an experienced technician and those prepared
using the automatic dilution feature of the SIL-30AC. Those results are
4-3. Entries for Standard Solution shown in Table 3.
Analysis Dilution Template *1 Dilution Accuracy (%) = caffeine peak area in standard solution using SIL-30AC ÷
caffeine peak area in standard solution prepared manually × 100
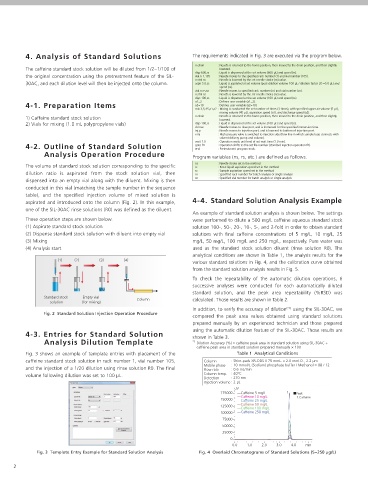
Fig. 3 shows an example of template entries with placement of the Table 1 Analytical Conditions
caffeine standard stock solution in rack number 1, vial number 105, Column : Shim-pack XR-ODS II 75 mmL. x 2.0 mmI.D., 2.2 µm
Mobile phase : 10 mmol/L (Sodium) phosphate buffer / Methanol = 88 / 12
and the injection of a 1/20 dilution using rinse solution R0. The final Flow rate : 0.6 mL/min
volume following dilution was set to 100 µL. Column temp. : 40°C
Detection : 270 nm
Injection volume : 2 µL
uV
175000 —Caffeine 5 mg/L 1 ˙Peak
—Caffeine 10 mg/L 1.Caffeine
150000 —Caffeine 25 mg/L
—Caffeine 50 mg/L
125000
—Caffeine 100 mg/L
100000 —Caffeine 250 mg/L
75000
50000
25000
0
0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0 min
Fig. 3 Template Entry Example for Standard Solution Analysis Fig. 4 Overlaid Chromatograms of Standard Solutions (5−250 µg/L)
2