Page 27 - Shimadzu-MassSpectrometerCatalog
P. 27
GCMS
Analysis of Residual Pesticides in Food Using Twin Line-GC/MS
By using a twin line system, two columns can be installed in a GC-MS. Switching between the columns is accomplished simply by changing
settings. To analyze pesticides in foods, two columns with different types of solid phases were installed using the twin lines. By comparing Software - LCMS -
the results obtained from each column, reliability can be increased for both quantitative and qualitative analysis. In particular, if a pesticide
overlaps with an impurity, in some cases the second column enables separation with a different type of solid phase. Therefore, comparing
data from two columns makes data analysis easier and improves reliability.
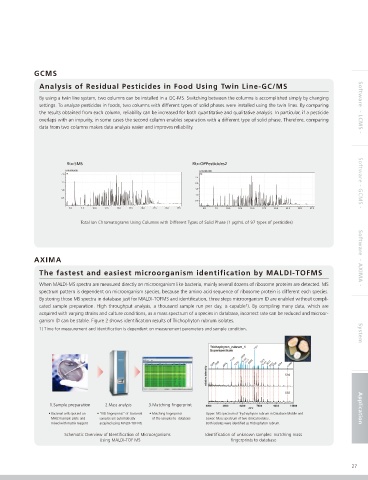
Rtx-5MS Rtx-OPPesticides2
(x10,000,000) (x10,000,000)
2.0 TIC TIC
2.5
1.5 Software - GCMS -
2.0
1.5
1.0
1.0
0.5
0.5
5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 17.5 20.0 22.5 25.0 27.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 17.5 20.0 22.5 25.0 27.5
Total Ion Chromatograms Using Columns with Different Types of Solid Phase (1 µg/mL of 97 types of pesticides)
AXIMA Software - AXIMA -
The fastest and easiest microorganism identification by MALDI-TOFMS
When MALDI-MS spectra are measured directly on microorganism like bacteria, mainly several dozens of ribosome proteins are detected. MS
spectrum pattern is dependent on microorganism species, because the amino acid sequence of ribosome protein is different each species.
By storing those MS spectra in database just for MALDI-TOFMS and identification, three steps microorganism ID are enabled without compli-
cated sample preparation. High throughput analysis, a thousand sample run per day, is capable 1 ). By compiling many data, which are
acquired with varying strains and culture conditions, as a mass spectrum of a species in database, incorrect rate can be reduced and microor-
ganism ID can be stable. Figure 2 shows identification results of Trichophyton rubrum isolates.
1) Time for measurement and identification is dependent on measurement parameters and sample condition. System
1.Sample preparation 2.Mass analysis 3.Matching fingerprint Application
• Bacterial cells spotted on • “MS fingerprints” of bacterial • Matching fingerprints Upper: MS spectrum of Trychophyton rubrum in Database Middle and
MALDI sample plate and samples are automatically of the samples to database Lower: Mass spectrum of two clinical isolates .
mixed with matrix reagent acquired using MALDI-TOF MS Both isolates were identified as Trichophyton rubrum.
Schematic Overview of Identification of Microorganisms Identification of unknown samples: matching mass
Using MALDI-TOF MS fingerprints to database
27