Page 9 - Shimadzu Journal vol.3 Issue2
P. 9
Metabolomics
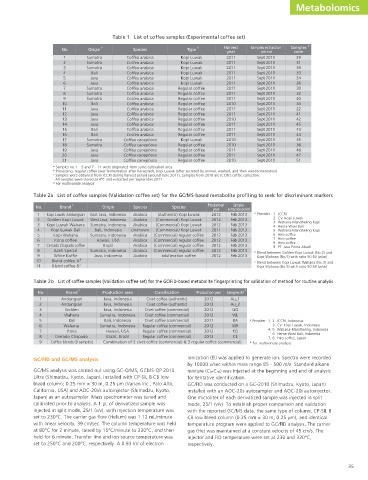
Table 1 List of coffee samples (Experimental coffee set)
a b Harvest Samples extraction c Samples d
No. Origin Species Type
year period code
1 Sumatra Coffea arabica Kopi Luwak 2011 Sept 2011 29
2 Sumatra Coffea arabica Kopi Luwak 2011 Sept 2011 31
3 Sumatra Coffea arabica Kopi Luwak 2011 Sept 2011 39
4 Bali Coffea arabica Kopi Luwak 2011 Sept 2011 33
5 Java Coffea arabica Kopi Luwak 2011 Sept 2011 24
6 Java Coffea arabica Kopi Luwak 2011 Sept 2011 26
7 Sumatra Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 30
8 Sumatra Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 32
9 Sumatra Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 40
10 Bali Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2010 Sept 2011 34
11 Java Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 22
12 Java Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 41
13 Java Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2010 Sept 2011 42
14 Java Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 45
15 Bali Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 43
16 Bali Coffea arabica Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 44
17 Sumatra Coffea canephora Kopi Luwak 2010 Sept 2011 35
18 Sumatra Coffea canephora Regular coffee 2010 Sept 2011 36
19 Java Coffea canephora Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 46
20 Java Coffea canephora Regular coffee 2011 Sept 2011 47
21 Java Coffea canephora Regular coffee 2010 Sept 2011 51
a Samples no.1 – 5 and 7 – 11 were originated from same cultivation area
b Processing: regular coffee (wet fermentation after harvested), Kopi Luwak (after secreted by animal, washed, and then wet-fermentation)
c Samples were obtained from ICCRI during harvest period (around June 2011). Samples from 2010 are ICCRI’s coffee collection.
All samples were stored at 4°C and extracted per September 2011
d For multivariate analysis
Table 2a List of coffee samples (Validation coffee set) for the GC/MS-based metabolite profiling to seek for discriminant markers
a Production Samples
No. Brand Origin Species Species
year extraction period
1 Kopi Luwak Andungsari East Java, Indonesia Arabica (Authentic) Kopi Luwak 2012 Feb 2013 a Provider 1 ICCRI
2 Golden Kopi Luwak West Java, Indonesia Arabica (Commercial) Kopi Luwak 2012 Feb 2013 2 CV. Kopi Luwak
3 Wahana-Mandheling Kopi
3 Kopi Luwak Wahana Sumatra, Indonesia Arabica (Commercial) Kopi Luwak 2012 Feb 2013 4 Hema-Wiwi Bali
4 Kopi Luwak Bali Bali, Indonesia Unknown (Commercial) Kopi Luwak 2011 Feb 2013 5 Wahana-Mandheling Kopi
5 Kopi Wahana Sumatra, Indonesia Arabica (Commercial) regular coffee 2012 Feb 2013 6 Hiro coffee
6 Kona coffee Hawaii, USA Arabica (Commercial) regular coffee 2012 Feb 2013 7 Hiro coffee
8 Hiro coffee
7 Cerrado Chapado coffee Brazil Arabica (Commercial) regular coffee 2012 Feb 2013 9 PT. Java Prima Abadi
8 Aceh Special Sumatra, Indonesia Arabica (Commercial) regular coffee 2012 Feb 2013 b Blend between Golden Kopi Luwak (No.2) and
9 White Koffie Java, Indonesia Arabica adulteration coffee 2012 Feb 2013 Kopi Wahana (No.5) with ratio 50:50 (w/w)
10 Blend coffee A b c Blend between Kopi Luwak Wahana (No.3) and
11 Blend coffee B c Kopi Wahana (No.5) with ratio 50:50 (w/w)
Table 2b List of coffee samples (Validation coffee set) for the GC/FID-based metabolite fingerprinting for validation of method for routine analysis
a b
No. Brand Production area Classification Production year Samples ID
1 Andungsari Java, Indonesia Civet coffee (authentic) 2012 Au_1
2 Andungsari Java, Indonesia Civet coffee (authentic) 2013 Au_2
3 Golden Java, Indonesia Civet coffee (commercial) 2012 GO
4 Wahana Sumatra, Indonesia Civet coffee (commercial) 2012 WL
5 Bali Bali, Indonesia Civet coffee (commercial) 2011 BA a Provider 1, 2 ICCRI, Indonesia
6 Wahana Sumatra, Indonesia Regular coffee (commercial) 2012 WR 3 CV. Kopi Luwak, Indonesia
4, 5 Wahana-Mandheling, Indonesia
7 Kona Hawaii, USA Regular coffee (commercial) 2012 KO
6 Hema-Wiwi Bali, Indonesia
8 Cerrado Chapado Brazil, Brazil Regular coffee (commercial) 2012 CE 7, 8 Hiro coffee, Japan
9 Coffee blends (9 samples) Combination of 3 civet coffee (commercial) & 3 regular coffee (commercial) b For multivariate analysis
GC/FID and GC/MS analysis ionization (EI) was applied to generate ion. Spectra were recorded
by 10000 u/sec within mass range 85 - 500 m/z. Standard alkane
GC/MS analysis was carried out using GC-Q/MS, GCMS-QP 2010 mixture (C8-C40) was injected at the beginning and end of analysis
Ultra (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan), installed with CP-SIL 8 CB low for tentative identification.
bleed column; 0.25 mm × 30 m, 0.25 µm (Varian Inc., Palo Alto, GC/FID was conducted on a GC-2010 (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan)
California, USA) and AOC-20i/s autoinjector (Shimadzu, Kyoto, installed with an AOC-20s autosampler and AOC-20i autoinjector.
Japan) as an autosampler. Mass spectrometer was tuned and One microliter of each derivatized sample was injected in split
calibrated prior to analysis. A 1 µL of derivatized sample was mode, 25/1 (v/v). To establish proper comparison and validation
injected in split mode, 25/1 (v/v), with injection temperature was with the reported GC/MS data, the same type of column, CP-SIL 8
set to 230°C. The carrier gas flow (Helium) was 1.12 mL/minute CB low bleed column (0.25 mm × 30 m, 0.25 µm), and identical
with linear velocity, 39 cm/sec. The column temperature was held temperature program were applied to GC/FID analysis. The carrier
at 80°C for 2 minute, raised by 15°C/minute to 330°C, and then gas (He) was maintained at a constant velocity of 45 cm/s. The
held for 6 minute. Transfer line and ion source temperature was injector and FID temperature were set at 230 and 320°C,
set to 250°C and 200°C, respectively. A 0.93 kV of electron respectively.
35