Page 10 - Shimadzu Journal vol.3 Issue2
P. 10
Metabolomics
Data preprocessing Multivariate data analysis
Chromatographic data from GC/MS were converted into ANDI files The details on discriminant marker identification for Kopi Luwak
(Analytical Data Interchange Protocol, *.cdf). This feature include in authentication by means of multivariate analyses, namely PCA and
GC/MS Solution software (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). These ANDI files OPLS-DA, have been described elsewhere . Briefly, the coffee bean data
1
were subjected to freely available software, MetAlign version 041011, sets were subjected to supervised discriminant analysis, Orthogonal
to perform peak detection, baseline correction and peak alignment of projection to latent structures-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA).
15
retention times . Spectra were normalized manually by adjusting the OPLS-DA was selected to seek and select statistically significant
peak intensity of each sample with internal standard, ribitol. Retention discriminant markers for Kopi Luwak authentication. To confirm
indexes of eluted compounds were calculated based on standard selection of significant compounds by OPLS-DA, data were also
alkane mixture. By comparing its retention indexes and unique mass subjected to MetaboAnalyst 2.0 to perform signifincance analysis of
spectra with in-house reference library constructed from 500 authentic microarrays/metabolites (SAM).
standard chemicals, tentative identification was performed. For Multivariate analysis was carried out using SIMCA-P+ ver. 13 (Umetrics,
comparison with NIST library, retention time was used instead. To Umeå, Sweden) to reduce dimensionality of the huge MS data and
simplify and accelerate tentative-identification with compounds that extract biological interpretation. PCA and OPLS-DA were used to
registered in in-house library database, AIoutput2 version 1.29, decipher the relationships between two data matrices, X (predicted
12
annotation software developed by authors’ laboratory, was utilized . variables), and Y (observed variables) . Here, the chromatographic
10
Raw chromatographic data of GC/FID were converted into CDF format GC/FID data were used as X and for Y, the binary vector of 0 and 1 was
using GCMS Solution software package (Shimadzu, Kyoto, Japan). The assigned for civet coffee and regular coffee, respectively. The data
converted files were subjected to baseline correction, normalization were Pareto scaled prior to analysis without any transformation.
and alignment of retention times using the in-house software,
PiroTran ver 1.41 (GL Sciences, Tokyo, Japan). The retention time of
3. Results and Discussion
internal standard ribitol was confirmed with co-injection of authentic
chemical standard before being utilized as reference for normalization GC/MS-based metabolite profiling of Kopi Luwak
and retention time alignment. To reduce the run-to-run variation, the
threshold for peak intensity (RSD) was set to < 20%, in each GC-Q/MS analysis was performed on aqueous extracts of Kopi Luwak
measurement replicate. To construct the data matrix, in which each and regular coffee bean to investigate the differences in their
row and column represent the samples and relative peak intensity at metabolite profiles to select discriminant marker for robust
certain retention time, respectively, the outcome data were imported authentication. Quadrupole mass spectrometer (Q/MS) was selected
into Pirouette ver 4.0 (Infometrix, Inc, Woodinville, Washington, USA). due to its availability as the most widely used mass analyzer.
The data matrix was then subjected to multivariate analysis. Therefore, the application of GC/Q-MS is expected to meet with
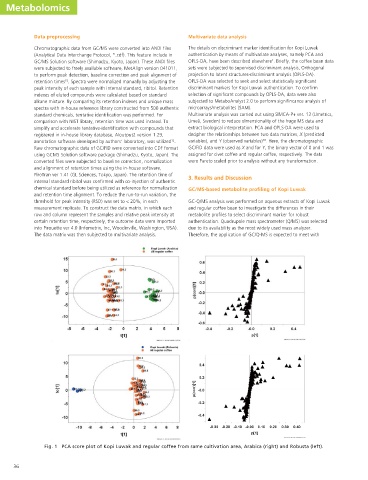
Fig. 1 PCA score plot of Kopi Luwak and regular coffee from same cultivation area, Arabica (right) and Robusta (left).
36