Page 71 - Application Notebook - Solution for Food Safety
P. 71
Application No.C105
News
n Analysis of Sulfamic Acid in Fertilizers
We verified the applicability of the LC/MS method using Sample 1.00 g
a byproduct compound fertilizer as an actual sample.
The permissible content level of sulfamic acid is set
based on the total amount of the principal component Water 100 mL
in each type of fertilizer. Here, taking the lower limit of
quantitation of sulfamic acid in fertilizer as 1/5 the
value of the minimum concentration permissible Shake (30 minutes)
(sulfamic acid concentration 0.005 % per principal
component 1 %), we conducted spike and recovery
testing using a spike quantity equivalent to the lower
limit of quantitation. Dilution × 100
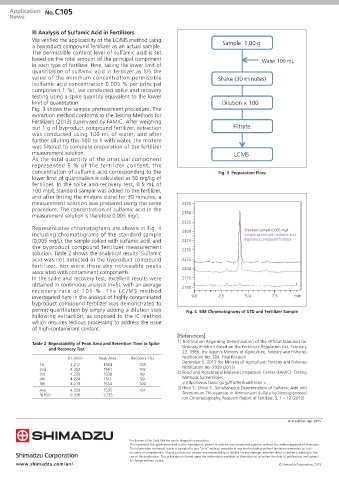
Fig. 3 shows the sample pretreatment procedure. The
extraction method conforms to the Testing Methods for
Fertilizers (2013) supervised by FAMIC. After weighing
out 1 g of byproduct compound fertilizer, extraction Filtrate
was conducted using 100 mL of water, and after
further diluting this 100 to 1 with water, the mixture
was filtered to complete preparation of the fertilizer
measurement solution. LCMS
As the total quantity of the principal component
represented 5 % of the fertilizer content, the
concentration of sulfamic acid corresponding to the Fig. 3 Preparation Flow
lower limit of quantitation is calculated as 50 mg/kg of
fertilizer. In the spike and recovery test, 0.5 mL of
100 mg/L standard sample was added to the fertilizer,
and after letting the mixture stand for 30 minutes, a
measurement solution was prepared using the same 2375
procedure. The concentration of sulfamic acid in the
measurement solution is therefore 0.005 mg/L. 2350
2325
Representative chromatograms are shown in Fig. 4 Standard sample 0.005 mg/L
including chromatograms of the standard sample 2300 Sample spiked with sulfamic acid
(0.005 mg/L), the sample spiked with sulfamic acid, and 2275 Byproduct compound fertilizer
the byproduct compound fertilizer measurement
solution. Table 2 shows the analytical results. Sulfamic 2250
acid was not detected in the byproduct compound 2225
fertilizer, nor were there any noticeable peaks
associated with contaminant components. 2200
In the spike and recovery test, excellent results were 2175
obtained in continuous analysis (n=5), with an average 2150
recovery rate of 101 %. The LC/MS method
investigated here in the analysis of highly contaminated 0.0 2.5 5.0 7.5 min
byproduct compound fertilizer was demonstrated to
permit quantitation by simply adding a dilution step Fig. 4 SIM Chromatograms of STD and Fertilizer Sample
following extraction, as opposed to the IC method
which requires tedious processing to address the issue
of high-contaminant content.
[References]
Table 2 Repeatability of Peak Area and Retention Time in Spike 1) Notification Regarding Determination of the Official Standard for
Ordinary Fertilizer Based on the Fertilizers Regulation Act, February
and Recovery Test
22, 1986, the Japan's Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries
R.t (min) Peak Area Recovery (%) Notification No. 284, Final Revision
December 5, 2013 the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries
1st 4.217 1564 103 Notification No. 2939 (2013)
2nd 4.252 1561 102
3rd 4.229 1508 99 2) Food and Agricultural Materials Inspection Center (FAMIC): Testing
4th 4.224 1511 99 Methods for Fertilizers
5th 4.219 1534 100 < http://www.famic.go.jp/ffis/fert/sub9.html >
3) Hiroi T., Shirai Y.: Simultaneous Determination of Sulfamic Acid and
Ave 4.228 1535 101 Ammonium Thiocyanate in Ammonium Sulfate by Nonsuppressed
%RSD 0.336 1.735
Ion Chromatography, Research Report of Fertilizer, 5, 1 – 12 (2012)
First Edition: Apr. 2015
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu.
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject
to change without notice.
www.shimadzu.com/an/ © Shimadzu Corporation, 2015