Page 21 - 5_TOC in daily practice
P. 21
Sum parameter – Total Organic Carbon
TOC determination with wet chemical UV-oxidation
SCA-130-511
Two oxidation techniques are now commonly
used in TOC analysis: catalytic combustion
and wet-chemical oxidation.
In catalytic combustion, carbon compounds
are converted to CO 2 using high
temperatures and a catalyst, with subsequent
detection of the resulting CO 2 using an NDIR
detector.
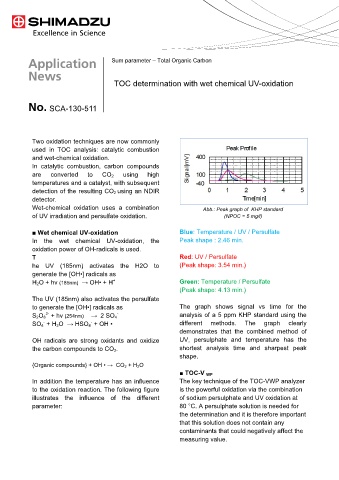
Wet-chemical oxidation uses a combination Abb.: Peak graph of KHP standard
of UV irradiation and persulfate oxidation. (NPOC = 5 mg/l)
■ Wet chemical UV-oxidation Blue: Temperature / UV / Persulfate
In the wet chemical UV-oxidation, the Peak shape : 2.46 min.
oxidation power of OH-radicals is used.
T Red: UV / Persulfate
he UV (185nm) activates the H2O to (Peak shape: 3.54 min.)
generate the [OH•] radicals as
+
H 2O + hv (185nm) → OH• + H Green: Temperature / Persulfate
(Peak shape: 4.13 min.)
The UV (185nm) also activates the persulfate
to generate the [OH•] radicals as The graph shows signal vs time for the
2-
-
S 2O 8 + hν (254nm) → 2 SO 4 analysis of a 5 ppm KHP standard using the
-
-
SO 4 + H 2O → HSO 4 + OH • different methods. The graph clearly
demonstrates that the combined method of
OH radicals are strong oxidants and oxidize UV, persulphate and temperature has the
the carbon compounds to CO 2. shortest analysis time and sharpest peak
shape.
{Organic compounds} + OH • → CO 2 + H 2O
■ TOC-V WP
In addition the temperature has an influence The key technique of the TOC-VWP analyzer
to the oxidation reaction. The following figure is the powerful oxidation via the combination
illustrates the influence of the different of sodium persulphate and UV oxidation at
parameter: 80 °C. A persulphate solution is needed for
the determination and it is therefore important
that this solution does not contain any
contaminants that could negatively affect the
measuring value.