Page 4 - Oligonucleotide Therapeutics Solution Guide
P. 4
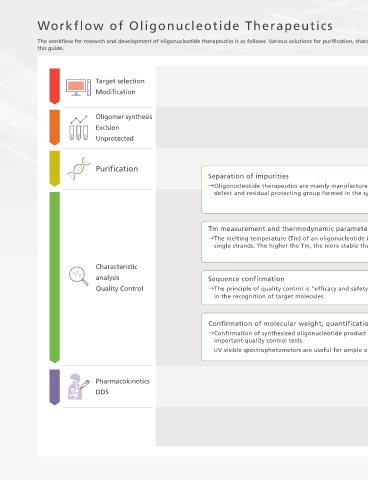
Workflow of Oligonucleotide Therapeutics
The workflow for research and development of oligonucleotide therapeutics is as follows. Various solutions for purification, characterization and quality control which are indispensable for the development of oligonucleotide therapeutics are introduced in
this guide.
Target selection
Modification Modification Target selection
Oligomer synthesis
Excision Unprotected Excision Oligomer synthesis
Unprotected
Purification Purification
Separation of impurities
→
Oligonucleotide therapeutics are mainly manufactured by chemical synthesis. Separation and purification from impurities such as base
defect and residual protecting group formed in the synthesis process are large problems.
P. 6 – 9
Tm measurement and thermodynamic parameter analysis Quality Control Characteristic analysis
→
The melting temperature (Tm) of an oligonucleotide is the temperature at which 50% of double-stranded DNA or RNA separates into
single strands. The higher the Tm, the more stable the double-stranded DNA or RNA. It is one of the quality control test items.
P. 10 – 13
Characteristic
analysis Sequence confirmation
Quality Control →
The principle of quality control is "efficacy and safety," and the sequence of oligonucleotides is an important factor because it is involved
in the recognition of target molecules. P. 14 – 17
Confirmation of molecular weight, quantification, and concentration
→
Confirmation of synthesized oligonucleotide product identity and examination of impurities by LC-MS precision mass spectrometry are
important quality control tests.
UV-visible spectrophotometers are useful for simple oligonucleotide concentration verification and spectral confirmation. P. 16 – 29
Pharmacokinetics DDS
DDS Other Pharmacokinetics