Page 4 - Pharmaceutical Solution for Pharma Analysis
P. 4
LAAN-A-LM-E108
Application Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry
News Development of a Phospholipid Profiling Method
Using Triple Quadrupole LC/MS/MS
No.C137
The lipid bilayer membrane structure of cell membranes phospholipid structure prediction based on molecular
is formed of phospholipids, with fatty acid chains ions (Fig. 1). The Shimadzu MRM library includes 422
st
oriented inside the membrane and polar groups situated constituents (1 method), and the phospholipid targets
on the membrane surface. Precursors of physiologically of the library are phosphatidylcholines (PC),
active lipids bound to phospholipids as fatty acids include phosphatidylethanolamines (PE), phosphatidylserines
polyunsaturated fatty acids such as arachidonic acid, (PS), phosphatidylglycerol (PG), phosphatidylinositol (PI),
EPA, and DHA. These lipids contribute to the formation and sphingomyelins (SM). A list of the fatty acids
of a wide variety of membrane structures. Due to recent included as analytical targets are shown in the table on
reports of a causal association between phospholipid the right in Fig. 1. A single chromatographic analysis can
compositions and various diseases, phospholipid profiling be used to profile 422 phospholipid constituents. The
techniques have gained interest as an important MRM library also includes 867 MRM transitions that are
approach in disease marker screening and disease needed to determine the fatty acid composition. The
st
mechanism identification. phospholipid profiling workflow begins with the 1
nd
Shimadzu has created a phospholipid profiling LC/MS/ method, after which the 2 method is performed if the
MS MRM library for the classification of phospholipids in fatty acid composition analysis is needed. Shimadzu has
biological samples. Phospholipids are divided into also created the MRM Event Link Editor that edits MRM
nd
glycerophospholipids and sphingophospholipids. methods, and is needed to create a 2 method from the
Qualitative analysis of phospholipids by MS/MS involves 867 MRM library transitions.
phospholipid classification via the detection of product The library allows for easy phospholipid profiling with a
ions created by polar group elimination, such as choline triple quadrupole mass spectrometer, and stress-free
and ethanolamine elimination, and subsequent fatty acid composition analysis.
nd
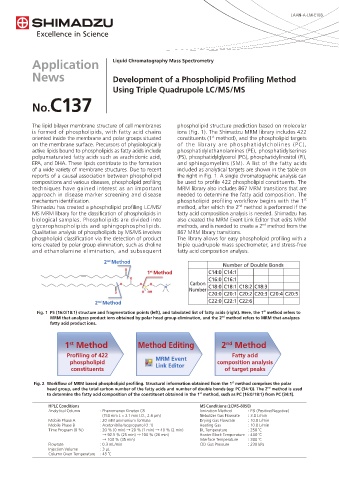
2 Method
Number of Double Bonds
1 Method C14:0 C14:1
st
C16:0 C16:1
+ Carbon C18:0 C18:1 C18:2 C18:3
Number
C20:0 C20:1 C20:2 C20:3 C20:4 C20:5
nd
2 Method C22:0 C22:1 C22:6
st
Fig. 1 PS (16:0/18:1) structure and fragmentation points (left), and tabulated list of fatty acids (right). Here, the 1 method refers to
MRM that analyzes product ions obtained by polar head group elimination, and the 2 method refers to MRM that analyzes
nd
fatty acid product ions.
st
nd
1 Method Method Editing 2 Method
Profiling of 422 MRM Event Fatty acid
phospholipid Link Editor composition analysis
constituents of target peaks
st
Fig. 2 Workflow of MRM based phospholipid profiling. Structural information obtained from the 1 method comprises the polar
nd
head group, and the total carbon number of the fatty acids and number of double bonds (eg: PC (34:1)). The 2 method is used
st
to determine the fatty acid composition of the constituent obtained in the 1 method, such as PC (16:0/18:1) from PC (34:1).
)1-$ $POEJUJPOT .4 $POEJUJPOT -$.4
Analytical Column : Phenomenex Kinetex C8 Ionization Method : ESI (Positive/Negative)
(150 mm L × 2.1 mm I.D., 2.6 μm) Nebulizer Gas Flowrate : 3.0 L/min
Mobile Phase A : 20 mM ammonium formate Drying Gas Flowrate : 10.0 L/min
Mobile Phase B : Acetonitrile/Isopropanol (1:1) Heating Gas : 10.0 L/min
Time Program (B %) : 20 % (0 min) ˠ 20 % (1 min) ˠ 40 % (2 min) DL Temperature : 250 ˚C
ˠ 92.5 % (25 min) ˠ 100 % (26 min) Heater Block Temperature : 400 ˚C
ˠ 100 % (35 min) Interface Temperature : 300 ˚C
Flowrate : 0.3 mL/min CID Gas Pressure : 230 kPa
Injection Volume : 3 μL
Column Oven Temperature : 45 ˚C