Page 14 - Shimadzu Journal vol.7 Issue2
P. 14
Food Development
Determination of garlic phenolic compounds using supercritical
fluid extraction coupled to supercritical fluid chromatography/
tandem mass spectrometry
Jian Liu , Feng Ji , Fengming Chen , Wei Guo , Minli Yang , Shengxiong Huang , Feng Zhang *, Yongsheng Liu *
c
a
a
a
b
a
b
a,b
a Institute of Food Safety, Chinese Academy of Inspection & Quarantine, Beijing 100176, China
b School of Food Science and Engineering, Hefei University of Technology, Hefei 230009, China
c Shimadzu (China) Co., LTD., Beijing, 100020, China
Introduction
Garlic (Allium sativum L.) has been widely cultivated and consumed phenolic compounds, with all of the compounds exhibiting
throughout the world as an important vegetable [1,2] . The physiological satisfactory separation effects, gradient times, and perfect
functions of garlic are likely due to its bioactive composition, such as peak shapes. The diol group bonded in the Diol column provides a
organosulfur compounds, vitamins, saponins, alkaloids and flavonoids polar and neutral character to the column and offers appropriate
[3,4] . Since phenolic compounds have significant bioactivity and play interaction with the hydroxyl group in the phenolic compounds.
vital roles in food, a simple, accurate, and green environmental technique The elution order observed was (1) ferulic acid, (2) p-coumaric
for analyzing phenolic compounds is needed. Conventional sample acid, (3) naringenin, (4) apigenin, (5) protocatechuic acid, (7)
preparation, such as traditional solvents, ultrasound, microwaves, isorhamnetin, (8) luteolin, (9) phthalic acid, and (11) quercetin.
ultrahigh pressure and enzymes have all been applied to extract of The Shim-pack UC-X Diol column was selected as the most
phenolic compounds from plants or foods [5,6] , despite the complex suitable chromatographic column for the separation of the
composition and unstable structure of phenolic compounds. Recently, phenolic compounds.
supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) has been widely applied in the ʢʷ ʣ ʢʷ ʣ
extraction or separation of bioactive components, due to the powerful
physicochemical properties of supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2),
which is the most commonly employed supercritical fluid . SC-CO2
[7]
can also be employed as the mobile phase for chromatographic
analysis, which is known as supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC).
SFC demonstrates an outstanding isolation capacity for compounds
with a wide range of polarities when using a mixture of SC-CO2 and
organic solvents as the mobile phase . In this study, an off-line
[8]
SFE-SFC-MS/MS method has been established for the analysis of
phenolic compounds in garlic using a Shimadzu Nexera-UC system NJO NJO
(Shimadzu, Japan); the extraction of phenolic compounds was first ʢʷ ʣ ʢʷ ʣ
performed using an automatic SFE process, and then the extracted
component was analyzed by SFC-MS/MS. Finally, the method was
validated and employed for the measurement of the phenolic
compounds present in garlic.
Optimization of SFC-MS/MS condition
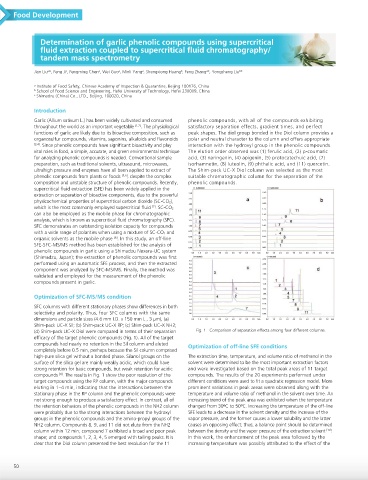
SFC columns with different stationary phases show differences in both
selectivity and polarity. Thus, four SFC columns with the same
dimensions and particle sizes (4.6 mm I.D. x 150 mm L., 3 µm), (a) NJO NJO
Shim-pack UC-X Sil; (b) Shim-pack UC-X RP; (c) Shim-pack UC-X NH2;
(d) Shim-pack UC-X Diol were compared in terms of their separation Fig. 1 Comparison of separation effects among four different columns.
efficacy of the target phenolic compounds (Fig. 1). All of the target
compounds had nearly no retention in the Sil column and eluted Optimization of off-line SFE conditions
completely before 0.5 min, perhaps because the Sil column comprised
high-pure silica gel without a bonded phase. Silanol groups on the The extraction time, temperature, and volume ratio of methanol in the
surface of the silica gel are mainly weakly acidic, which could have solvent were determined to be the most important extraction factors
strong retention for basic compounds, but weak retention for acidic and were investigated based on the total peak areas of 11 target
compounds . The results in Fig. 1 show the poor resolution of the compounds. The results of the 20 experiments performed under
[9]
target compounds using the RP column, with the major compounds different conditions were used to fit a quadratic regression model. More
eluting in 1–4 min, indicating that the interactions between the prominent variations in peak areas were observed along with the
stationary phase in the RP column and the phenolic compounds were temperature and volume ratio of methanol in the solvent over time. An
not strong enough to produce a satisfactory effect. In contrast, all of increasing trend of the peak area was exhibited when the temperature
the retention behaviors of the phenolic compounds in the NH2 column changed from 30C to 50C. Increasing the temperature of the off-line
were probably due to the strong interactions between the hydroxyl SFE leads to a decrease in the solvent density and the increase of the
groups in the phenolic compounds and the amino-propyl groups of the vapor pressure, and the former causes a lower solubility and the latter
NH2 column. Compounds 8, 9, and 11 did not elute from the NH2 causes an opposing effect; thus, a balance point should be determined
[10]
column within 12 min; compound 7 exhibited a broad and poor peak between the density and the vapor pressure of the extraction solvent .
shape; and compounds 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 emerged with tailing peaks. It is In this work, the enhancement of the peak area followed by the
clear that the Diol column presented the best resolution for the 11 increasing temperature was possibly attributed to the effect of the
50