Page 40 - Shimadu Consumables Catalog
P. 40
UHPLC/HPLC Columns
Shim-pack MAqC-ODS
Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I reversed-phase columns are packed with a silica gel containing metal and bonded octadecylsilyl group.
In addition to the hydrophobic characteristics of the ODS, the metal content also provides cation-exchange effects. This increases the
retention of basic compounds. Therefore, this allows use with only a buffer solution as the mobile phase for analyses that previously
required using an ion pair reagent and enables using gradient elution. These characteristics are especially beneficial for analyzing
water soluble vitamins and pharmaceuticals that contain a large amount of basic compounds.
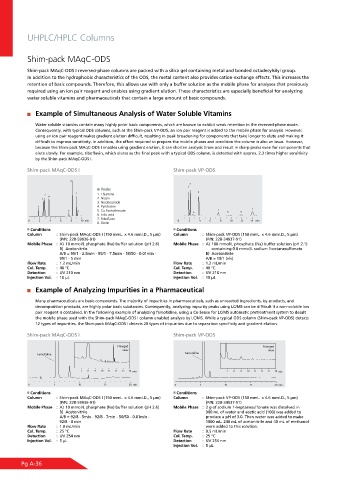
Example of Simultaneous Analysis of Water Soluble Vitamins
Water soluble vitamins contain many highly polar basic components, which are known to exhibit weak retention in the reversed-phase mode.
Consequently, with typical ODS columns, such as the Shim-pack VP-ODS, an ion pair reagent is added to the mobile phase for analysis. However,
using an ion pair reagent makes gradient elution difficult, resulting in peak broadening for components that take longer to elute and making it
difficult to improve sensitivity. In addition, the effort required to prepare the mobile phases and condition the column is also an issue. However,
because the Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I enables using gradient elution, it can shorten analysis times and result in sharp peaks even for components that
elute slowly. For example, riboflavin, which elutes as the final peak with a typical ODS column, is detected with approx. 2.3 times higher sensitivity
by the Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I.
Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I Shim-pack VP-ODS
Peaks
1. Thiamine
2. Niacin
3. Nicotinamide
4. Pyridoxine
5. Ca Pantothenate
6. Folic acid
7. Riboflavin
8. Biotin
Conditions Conditions
Column : Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I (150 mmL. × 4.6 mmI.D., 5 μm) Column : Shim-pack VP-ODS (150 mmL. × 4.6 mmI.D., 5 μm)
(P/N: 228-59936-91) (P/N: 228-34937-91)
Mobile Phase : A) 10 mmol/L phosphate (Na) buffer solution (pH 2.6) Mobile Phase : A) 100 mmol/L phosphate (Na) buffer solution (pH 2.1)
B) Acetonitrile containing 0.8 mmol/L sodium 1-octanesulfonate
A/B = 99/1 - 2.5min - 99/1 - 7.5min - 50/50 - 0.01min - B) Acetonitrile
99/1 - 5 min A/B = 10/1 (v/v)
Flow Rate : 1.2 mL/min Flow Rate : 1.2 mL/min
Col. Temp. : 40 °C Col. Temp. : 40 °C
Detection : UV 210 nm Detection : UV 210 nm
Injection Vol. : 10 μL Injection Vol. : 10 μL
Example of Analyzing Impurities in a Pharmaceutical
Many pharmaceuticals are basic compounds. The majority of impurities in pharmaceuticals, such as unreacted ingredients, by-products, and
decomposition products, are highly polar basic substances. Consequently, analyzing impurity peaks using LC/MS can be difficult if a non-volatile ion
pair reagent is contained. In the following example of analyzing famotidine, using a Co-Sense for LC/MS automatic pretreatment system to desalt
the mobile phase used with the Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I column enabled analysis by LC/MS. While a typical ODS column (Shim-pack VP-ODS) detects
12 types of impurities, the Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I detects 20 types of impurities due to separation specificity and gradient elution.
Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I Shim-pack VP-ODS
Conditions Conditions
Column : Shim-pack MAqC-ODS I (150 mmL. × 4.6 mmI.D., 5 μm) Column : Shim-pack VP-ODS (150 mmL. × 4.6 mmI.D., 5 μm)
(P/N: 228-59936-91) (P/N: 228-34937-91)
Mobile Phase : A) 10 mmol/L phosphate (Na) buffer solution (pH 2.6) Mobile Phase : 2 g of sodium 1-heptanesulfonate was dissolved in
B) Acetonitrile 900 mL of water and acetic acid (100) was added to
A/B = 92/8 - 5min - 92/8 - 7min - 50/50 - 0.01min - produce a pH of 3.0. Then water was added to make
92/8 - 8 min 1000 mL. 240 mL of acetonitrile and 40 mL of methanol
Flow Rate : 1.0 mL/min were added to this solution.
Col. Temp. : 25 °C Flow Rate : 0.5 mL/min
Detection : UV 254 nm Col. Temp. : 25 °C
Injection Vol. : 5 μL Detection : UV 254 nm
Injection Vol. : 5 μL
Pg A-36