Page 16 - Microorganism Species Analysis
P. 16
MALDI-TOF MS MALDI-TOF MS
Direct Measurements of Microorganism-Derived Components
Microorganism Solutions Microorganism Solutions
Data Data
Measurements of Peptides Batch Measurement of Yeast Metabolite Components Using the MALDI-TOF MS AXIMA Series
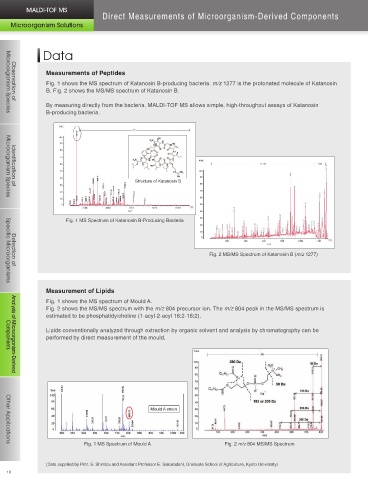
Fig. 1 shows the MS spectrum of Katanosin B-producing bacteria. m/z 1277 is the protonated molecule of Katanosin Microorganism Species Observation of
Test and research flow
B. Fig. 2 shows the MS/MS spectrum of Katanosin B.
1. Pick up some of the sake yeast from a single colony cultivated on the plate.
Observation of
By measuring directly from the bacteria, MALDI-TOF MS allows simple, high-throughput assays of Katanosin 2. Mix the yeast sample and matrix reagent on the AXIMA MALDI sample plate.
B-producing bacteria. 3. Perform mass spectrometry using the MALDI-TOF MS AXIMA Series.
Microorganism Species
In the direct MS measurement of the yeast, many
ions derived from biological components, believed
to be metabolite components, were observed in
the low-mass region (Fig. 1).
Lipid? Microorganism Species Identification of
Lipid?
Structure of Katanosin B
Identification of
Microorganism Species
Lipid?
Fig. 1 MS Spectrum of Katanosin B-Producing Bacteria
Fig. 2 MS/MS Spectrum of Katanosin B (m/z 1277) Fig. 1 MS Spectrum of Sake Yeast Specific Microorganisms Detection of
Detection of
Secondary Component
Specific Microorganisms
For ginjo
Measurement of Lipids (finely-brewed) sake
Fig. 1 shows the MS spectrum of Mould A. For normal sake
Fig. 2 shows the MS/MS spectrum with the m/z 804 precursor ion. The m/z 804 peak in the MS/MS spectrum is
estimated to be phosphatidylcholine (1-acyl-2-acyl 18:2-18:2). Alcohol-tolerant
Lipids conventionally analyzed through extraction by organic solvent and analysis by chromatography can be Primary Component
performed by direct measurement of the mould. Components Analysis of Microorganism-Derived
Fig. 3 Primary Component Analysis (PCA)
Components
Normal sake yeast
Analysis of Microorganism-Derived
The MS spectra were compared for several types
Ginjo (finely-brewed) of sake yeast (Fig. 2) and primary component
sake yeast
analysis (Fig. 3) was conducted.
The yeast strains were grouped based on the ions
Mould A strain detected, and citric acid and glutamic acid were
Alcohol-tolerant yeast
identified as candidate microorganism-derived Other Applications
components to characterize each yeast strain.
Fig. 1 MS Spectrum of Mould A Fig. 2 m/z 804 MS/MS Spectrum
Other Applications
Fig. 2 MS Spectra of Several Types of Sake Yeast
(Data supplied by Prof. S. Shimizu and Assistant Professor E. Sakuradani, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University) (Data supplied by Kizakura Co., Ltd.)
16 17