Page 60 - Application Handbook - Liquid Chromatography
P. 60
LAAN-A-LC-E227
Application High Performance Liquid Chromatography
News High Speed, High Resolution Analysis (Part 46)
Analysis of Pre-Column Derivatized Biogenic Amines
No.L449 by the Nexera SIL-30AC Autosampler
Biogenic amines are produced naturally by the Table 2 Analytical Conditions
enzymatic decarboxylation of amino acids in beverages
and food. Biogenic amines such as these are also used Column : Shim-pack XR-ODSⅢ (75 mm L. × 2.0 mm I.D., 1.6 µm)
Mobile Phase : A : 100 mmol/L Acetate (Sodium) Buffer (pH 4.7)
as an indicator of food spoilage. Histamine, a substance B : Acetonitrile
that can cause allergy-like food poisoning, must not Time Program : B.Conc. 15 % (0 min) →30 % (3 min) →40 % (8 min)
→15 % (8.01-11 min)
exceed 50 ppm in food in general according to FDA Flowrate : 0.5 mL/min
standards, 100 ppm in marine products in the EU, and Column Temp. : 40 °C
400 ppm in fish sauce according to the Codex Injection Vol. : 1 µL
International Food Standards. In addition, biogenic Detection : RF-20AXS Ex. at 330 nm, Em. at 440 nm
: 30 °C
Cell Temp.
amines such as cadaverine and tyramine appear to Flow Cell : Semi-micro cell
intensify the allergy-like food toxicity of histamine.
In Application News articles L432 and L437, we
introduced examples of the pretreatment functions of
the SIL-30AC autosampler in the analysis of
fluorescence-derivatized amino acids using 700
o-phthalaldehyde (OPA). Here, we introduce an 1
example of the analysis of fluorescent amines that were 600
derivatized with OPA. 2
500
n Simultaneous Determination of 7 Biogenic Amines 3
With this method, the pretreatment functions of the 400
Nexera SIL-30AC autosampler were utilized to conduct
automated derivatization of the amines using OPA. 300
Table 1 shows the derivatization reagents used with this 6
method, and Fig. 1 shows the reagent addition and 200 7
mixing settings that were used for automated 5
derivatization using the Nexera SIL-30AC autosampler. 100 4
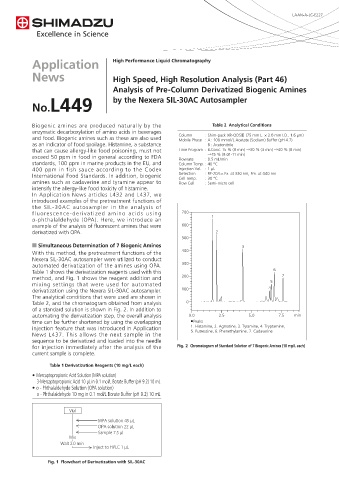
The analytical conditions that were used are shown in
Table 2, and the chromatogram obtained from analysis 0
of a standard solution is shown in Fig. 2. In addition to
automating the derivatization step, the overall analysis 0.0 2.5 5.0 7.5 min
time can be further shortened by using the overlapping ■Peaks
injection feature that was introduced in Application 1. Histamine, 2. Agmatine, 3. Tyramine, 4. Tryptamine,
News L437. This allows the next sample in the 5. Putrescine, 6. Phenethylamine, 7. Cadaverine
sequence to be derivatized and loaded into the needle
for injection immediately after the analysis of the Fig. 2 Chromatogram of Standard Solution of 7 Biogenic Amines (10 mg/L each)
current sample is complete.
Table 1 Derivatization Reagents (10 mg/L each)
• Mercaptopropionic Acid Solution (MPA solution)
3-Mercaptopropionic Acid 10 µL in 0.1 mol/L Borate Buffer (pH 9.2) 10 mL
• o - Phthalaldehyde Solution (OPA solution)
o - Phthalaldehyde 10 mg in 0.1 mol/L Borate Buffer (pH 9.2) 10 mL
Vial
MPA solution 45 µL
OPA solution 22 µL
Sample 7.5 µL
Mix
Wait 2.0 min
Inject to HPLC 1 µL
Fig. 1 Flowchart of Derivatization with SIL-30AC