Page 20 - Application Handbook - Liquid Chromatography
P. 20
HILIC×RP-LC for phospholipid (PL)
2-2. Reagents and Materials MS conditions 140000000 TIC( ) A 5. HILIC×RP-LC for phospholipid (PL)
5.
+
separation
MS acquisition performed using the ESI interface operating in both 4 separation
For the extraction procedure, chloroform and methanol were ob- 120000000
tained from VWR (Milan, Italy). positive and negative ionization modes:
100000000 After a proper optimization of the two different separation systems, an
mass spectral range: 200–1100 m/z; event time: 1 sec; scan speed: 6
For LC×LC–MS analyses, water, acetonitrile, methanol, tetrahydrofu- 80000000 HILIC×RP-LC system was tuned.
938 amu/s; nebulizing gas (N 2 ) ow: 1.5 L.min ; drying gas (N 2 ) ow:
−1
ran, isopropanol, all LC–MS grade, and formic acid were purchased 15 L.min ; interface temperature: 350°C; heat block temperature: 60000000 2 3 5 For both samples, the PC turned out the richest in terms of molecular
−1
from Riedel-de Haën (Seelze, Germany). Ammonium formate was ob- 1 species. As an example, an enlargement of the HILIC×RP-LC–ESI-MS
200°C; desolvation line (DL) temperature: 250°C; DL voltage: −34 V;
tained from Alfa Aesar GmbH & Co., KG (Karlsruhe, Germany). The pH probe voltage: +4.5 kV; Qarray DC voltage: 1 V; Qarray RF voltage: 40000000 contour plot, with the corresponding 2D raw data for the plasma
of buffered mobile phases was adjusted to 5.5 by adding a few drops 100 V; detection gain: 0.8 kV. 20000000 sample, is reported in Fig. 5. Up to sixteen and fourteen molecular spe-
of formic acid. The standards of phosphatidylinositol (PI), phosphatidyl- cies, belonging PC classes, over two 15 min modulation cycles were
0.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 25.0 30.0 min
serine (PS), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylcholine (PC), positively identied in cow’s milk and plasma samples, respectively. The
sphingomyielin (SM) and lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC) were pur- 3. Results and discussion 200000000 TIC( ) B observed chromatographic pattern ts to the expected PL separation
3. Results and discussion
+
chased from Sigma–Aldrich/Supelco (Bellefonte, PA, USA). based on increasing hydrophobicity, viz. increasing ECN values, rang-
175000000 ing from 26 to 34. It is worth mentioning that the employed 2D mobile
Chromatographic separations were carried out using different col- The objective of this work was to develop an HILIC×RP-LC system in 150000000 phase allowed to successfully separate also isobaric species. A list of the
umns provided by Supelco (Bellefonte, PA, USA): Ascentis Express combination with mass spectrometric detection for analysis of PL mo- 125000000
lecular species contained in Folch-extracted cow’s milk and plasma 4 major species contained in a phospholipid standard mixture, cow’s milk
HILIC (150 mmL. × 2.1 mmI.D., 2.7 µm d.p.), and Ascentis Express C18 100000000 sample and a plasma sample is reported in Table 1.
(150 mmL. × 4.6 mmI.D., 2.7 µm d.p.). samples. Prior to HILIC×RP-LC separations the two dimensions were 75000000 2
optimized independently. 5
50000000
2-3. LC×LC instrumentation and software 25000000 1 3
6
• Shimadzu CBM-20A controller 4. Optimization of D1 and D2 0.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 25.0 30.0
4. Optimization of D1 and D2
• two Shimadzu LC-20AD dual-plunger parallel-ow pumps separation systems min
separation systems
150000000
• Shimadzu LC-20AB dual-plunger parallel-ow pumps TIC( ) C
+
HILIC separation can be described either as liquid–liquid partition chro-
• Shimadzu DGU-20A5 degassing unit 125000000 4
matography, or a version of NP-LC, run with partially aqueous mobile
• Shimadzu CTO-20A column oven phases. Compounds are separated by passing normally an organic 100000000
• Shimadzu SIL-20AC autosampler mobile phaseacross a neutral hydrophilic stationary phase, thus solutes 75000000 5
are eluted in order of increasing hydrophilicity; the separation selectiv-
• Shimadzu SPD-M20A photo diode array detector (2.5 µL detector ow cell)
ity is, therefore, complementary to that in reversed phase mode. The 50000000 6
• Shimadzu LCMS-2020 mass spectrometer
use of higher-organic content mobile phases is advantageous in pro-
25000000
For connecting the two dimensions: 2-position 10-port switching viding larger diffusion constants of analytes during their migration 1 2
valve (Supelco, Bellefonte, PA, USA) placed inside the column oven through the column, allowing a partial separation of molecular species
0.0 5.0 10.0 15.0 20.0 25.0 30.0 min
and equipped with two identical 20 µL sample loops. and also better ionization efciency in electrospray ionization.
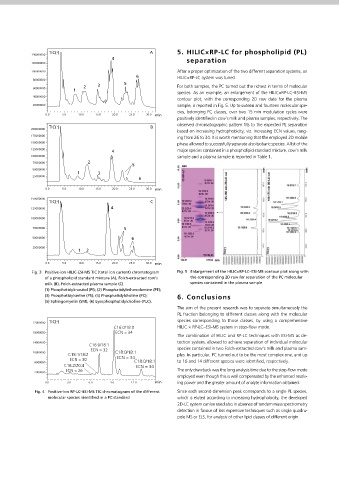
Fig. 3 Positive-ion HILIC-ESI-MS TIC (total ion current) chromatogram Fig. 5 Enlargement of the HILIC×RP-LC–ESI-MS contour plot along with
Fig. 3 shows the total ion current (TIC) chromatogram of a HILIC-ESI-MS
2-4. Software analysis of three different samples, namely, PL standard mixture (A), of a phospholipid standard mixture (A), Folch-extracted cow’s the corresponding 2D raw for separation of the PC molecular
species contained in the plasma sample
milk (B), Folch-extracted plasma sample (C)
• Shimadzu LabSolutions (Version 5.41 SP1) Folch-extracted cow’s milk (B), Folch-extracted plasma sample (C). Base- (1) Phosphatidylinositol (PI); (2) Phosphatidylethanolamine (PE);
line separation of the six PL classes was achieved, under gradient condi- (3) Phosphatidylserine (PS); (4) Phosphatidylcholine (PC); 6. Conclusions
Conclusions
6.
2-5. 2D Software tions, within a run time of 30 min, according to decreasing polarity viz. (5) Sphingomyelin (SM); (6) Lysophosphatidylcholine (PLC).
PI eluted rst followed by PE and PS; the PL classes, containing the phos- The aim of the present research was to separate simultaneously the
• ChromSquare (Version 2.0) from Chromaleont, Messina, Italy phocholine head group (PC, SM and LPC), were the most retained and PL fraction belonging to different classes along with the molecular
thus the latest to elute. Identication was carried out by the inspec- 22000000 TIC( ) species corresponding to those classes, by using a comprehensive
+
2-6. LC×LC-MS conditions tion of both [M+H] and [M−H] ions, the latter employed for better C16:0/18:0 HILIC × RP-LC–ESI-MS system in stop-ow mode.
−
+
D1 separations: Ascentis Express HILIC ionization of PI. 18000000 ECN = 34 The combination of HILIC and RP-LC techniques with ESI-MS as de-
Flow rate : 0.1 mL.mL −1 For the 2D separations, a C18 column packed with 2.7 mm particles 14000000 C16:0/18:1 tection system, allowed to achieve separation of individual molecular
Mobile phases : (A) acetonitrile/ammonium formate (10 mM) buffer pH ECN = 32 species contained in two Folch-extracted cow’s milk and plasma sam-
5.5 (90:10) and (B) acetonitrile/methanol/ammonium was employed. RP-LC separation is mainly achieved on the basis of the 10000000 C18:1/18:2 C18:0/18:1 ples. In particular, PC turned out to be the most complex one, and up
formate (10 mM) buffer pH 5.5 (55:35:10) difference in chain length and the number of fatty acid double bonds ECN = 30 ECN = 34
Gradient elution : 0 min, 0% B; 20 min, 0% B; 25 min, 100% B; 210 min, (i.e. essentially on the lipophilicity), viz. increasing equivalent carbon 6000000 C18:2/20:4 C18:0/18:1 to 16 and 14 different species were identi¥ed, respectively.
100% B; 211 min, 0% B number (ECN), dened as the total carbon number (CN) of fatty acids ECN = 26 ECN = 34 The only drawback was the long analysis time due to the stop-ow mode
Injection volume : 10 µL. 2000000
minus two times the double bond (DB) number (ECN = CN − 2DB). employed even though this is well compensated by the enhanced resolv-
D2 separations: Ascentis Express C18 0.0 3.0 6.0 9.0 12.0 min ing power and the greater amount of analyte information obtained.
Fig. 4 shows the TIC chromatogram from the positive-ion LC–ESI-MS
Mobile phase : (A) ammonium formate buffer (10 mM; pH 5.5)/
isopropanol/tetrahydrofuran (30:55:15) and (B) acetonitrile. analysis of a PC standard. Baseline separation of six of them was Fig. 4 Positive-ion RP-LC–ESI-MS TIC chromatogram of the different Since each second-dimension peak corresponds to a single PL species,
Isocratic elution (40% B) achieved, at a ow rate of 0.9 mL/min, under isocratic conditions, m olecular species identied in a PC standard which is eluted according to increasing hydrophobicity, the developed
Flow rate : 3.0 mL.min . Prior to MS detection, the mobile phase ow within a run time of 15 min. The retention of molecular species in- 2D-LC system can be used also in absence of tandem mass spectrometry
−1
−1
rate was reduced to 0.3 mL.mL through a T-piece union. detection in favour of less expensive techniques such as single quadru-
Modulation time of the switching valve : 15 min creased proportionally to the ECN, from 24 to 34). pole MS or ELS, for analysis of other lipid classes of different origin.
2