Page 21 - Application Handbook - Liquid Chromatography
P. 21
C190-E181
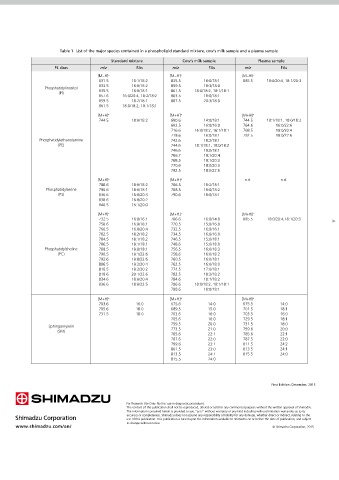
Table 1 List of the major species contained in a phospholipid standard mixture, cow’s milk sample and a plasma sample
Standard mixture Cow’s milk sample Plasma sample Stop- ow Comprehensive Two-dimensional
PL class m/z FAs m/z FAs m/z FAs
[M−H] − [M−H] − [M−H] − Technical Liquid Chromatography Combined with Mass
831.5 16:1/18:2 835.5 16:0/18:1 885.5 18:0/20:4, 18:1/20:3
833.5 16:0/18:2 859.5 18:3/18:0 Report
Phosphatidylinositol 835.5 16:0/18:1 861.5 18:0/18:2, 18:1/18:1 Spectrometric Detection for Phospholipid Analysis
(PI)
857.6 16:0/20:4, 18:2/18:2 863.5 18:0/18:1 LC×LC for phospholipids in milk and plasma samples
859.5 18:2/18:1 887.5 20:3/18:0
861.5 18:0/18:2, 18:1/18:1
Paola Dugo , Nermeen Fawzy , Francesco Cacciola , Paola Donato , Filomena Cichello , Luigi Mondello 1, 2
1
1, 2
1
1
1
[M+H] + [M+H] + [M+H] +
744.5 18:0/18:2 690.6 14:0/18:1 744.5 18:1/18:1, 18:0/18:2
692.5 16:0/16:0 764.6 16:0/22:6
716.6 16:0/18:2, 16:1/18:1 768.5 18:0/20:4
718.6 16:0/18:1 792.5 18:0/22:6 Abstract:
Phosphatidylethanolamine 742.6 18:2/18:1
(PE) 744.6 18:1/18:1, 18:0/18:2 A novel comprehensive two-dimensional liquid chromatographic (LC×LC) system for characterization of phospholipid (PL) molecular species
746.6 18:0/18:1 belonging to six phospholipid classes was developed. To tackle such a task, a silica hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC) column
766.7 18:1/20:4 was used as the rst dimension (D1), and reversed-phase liquid chromatography (RP-LC) with a C18 column was used as the second dimension
768.5 18:1/20:3 (D2) in combination with mass spectrometric detection. Fraction transfer from the D1 to the D2 was performed by means of a two-position
770.6 18:0/20:3 ten-port switching valve, operated under stop-ow conditions. The capability of the investigated LC×LC approach was demonstrated in the
792.5 18:0/22:6 separation of phospholipid molecular species contained in two Folch-extracted cow’s milk and plasma samples.
[M+H] + [M+H] + n.d. n.d. Keywords: comprehensive LC, phospholipids, mass spectrometry, stop- ow
788.6 18:0/18:2 786.5 18:2/18:1
Phosphatidylserine 790.6 18:0/18:1 788.5 18:0/18:2
(PS) 836.6 16:0/20:3 790.6 18:0/18:1
838.6 16:0/20:2
840.5 16:1/20:0
1. Introduction
2. Experimental
1. Intr oduction 2. Experimental
[M+H] + [M+H] + [M+H] +
732.5 16:0/16:1 706.6 16:0/14:0 885.5 18:0/20:4,18:1/20:3 2-1. Samples and sample preparation
758.6 16:0/18:1 720.5 15:0/16:0 Phospholipids (PLs) are an important class of biomolecules playing an
760.5 16:0/20:4 732.5 16:0/16:1 important functional, structural and metabolic role in the human
782.5 18:2/18:2 734.5 16:0/16:0 body as witnessed by recent studies which have given considerable A crude cow’s milk sample was provided by a Calabrian producer
784.5 18:1/18:2 746.5 15:0/18:1 evidence on the health-promoting effects such as antiinammatory whereas the plasma sample was kindly donated by a sane volunteer.
786.5 18:1/18:1 748.6 15:0/18:0
Phosphatidylcholine 788.5 18:0/18:1 756.5 16:0/18:3 activity and risk reduction of cardiovascular diseases. Extraction of the lipid fraction was carried out from 10 mL and 1.5
(PC) 790.5 18:1/22:6 758.6 16:0/18:2 Several analytical methods have been developed for characterization of mL, respectively, of the cow’s milk and plasma sample, according to
792.6 18:0/22:6 760.5 16:0/18:1 the Folch method in order to attain an exhaustive extraction of the
806.5 18:2/20:4 762.5 16:0/18:0 molecular species within different PL classes. From a chromatographic
810.5 18:2/20:2 774.5 17:0/18:1 stand-point, it must be noted that the employment of a single tech- whole lipid content. The total extract was evaporated under vacuum,
818.6 20:1/22:6 782.5 18:2/18:2 nique can only provide useful information on either the different phos- and the nal dry residue (400 and 150 mg for cow’s and donkey’s
834.6 18:0/20:4 784.6 18:1/18:2 pholipid classes or the molecular species within a particular PL class. milk, respectively) was re-dissolved in chloroform/methanol 2:1 (v/v)
836.6 18:0/22:5 786.6 18:0/18:2, 18:1/18:1
788.6 18:0/18:1 In this technical report, in order to simultaneously separate and identify and stored at –18 °C until use.
the different PL classes together with the separation and identication of
[M+H] + [M+H] + [M+H] +
703.6 16:0 675.6 14:0 675.5 14:0 the different molecular species within each class, a fully comprehensive
705.6 18:0 689.5 15:0 701.5 18:1 LC (LC×LC) method was developed for the rst time. Such a system
731.5 18:0 703.6 16:0 703.5 16:0 comprised of a silica hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography
705.6 16:0 729.5 18:1
759.5 20:0 731.5 18:0 (HILIC) column in the rst dimension (D1) and an octadecylsilica column
Sphingomyielin in the second dimension (D2) and was run under stop-ow conditions.
(SM) 773.5 21:0 759.6 20:0
785.6 22:1 785.6 22:1 The capability of such a system (Fig. 1) was evaluated for analysis of PLs
787.6 22:0 787.5 22:0 contained in two Folch-extracted cow’s milk and plasma samples (Fig. 2).
799.6 23:1 811.5 24:2
801.5 23:0 813.5 24:1
813.5 24:1 815.5 24:0
815.5 24:0
First Edition: December, 2015
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu. Fig. 2 Enlargement of the HILIC×RP-LC–ESI-MS contour plot for
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its separation of the phosphatidylethanolamine (PE),
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject Fig. 1 LC×LC/MS instrumentation along with the corresponding 2D raw data
to change without notice.
www.shimadzu.com/an/ © Shimadzu Corporation, 2015 1 University of Messina, Italy
2 Chromaleont S.r.l. 1