Page 18 - LifeScience Solution for FNIRS
P. 18
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Language Processing Functions Light to Measure Brain Function Principle of Using Near Infrared
Data Imaging Optical Brain-Function
Semantic Processing and Brain Functions in Chinese / Japanese Bilingual Subjects Results
There are some isomorphic words that are written the same in Japanese and Chinese but have different meanings. For example, ؿं When a Japanese / Chinese isomorphic word was presented to the bilingual subjects together with a picture representing the meaning
means "automobile" in Chinese but "steam train" in Japanese. We were able to confirm differences in brain function between in the non-target language (L1, Chinese), the false response rate (proportion falsely identified as the Japanese meaning) was higher
Chinese / Japanese bilingual subjects (first language (L1): Chinese, second language (L2): Japanese) and Japanese monolingual subjects than in the monolingual subjects. This result shows that the non-target language (L1) processing seems to interfere with the target bilitation Neuroreha-
(first language: Japanese) during the semantic processing of isomorphic words. language (L2) processing in bilingual subjects.
fNIRS measurements on the Chinese / Japanese bilingual subjects revealed lower activation of semantic information in the non-target Yes Response Rate
first language during processing targeting the second language in which the subject has a lower degree of proficiency.
JML BL
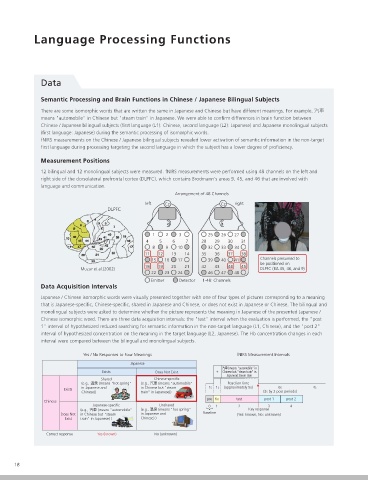
Measurement Positions Interference from L1 fNIRS and fMRI Comparison of
12 bilingual and 12 monolingual subjects were measured. fNIRS measurements were performed using 48 channels on the left and
right side of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), which contains Brodmann's areas 9, 45, and 46 that are involved with
language and communication. Known response (%)
Arrangement of 48 Channels
left Cz Cz right Motor Control Brain Activity during
DLPFC
Japanese-specific Shared Chinese-specific Unrelated
1 2 3 25 26 27 Hit False alarm
4 5 6 7 28 29 30 31 Two-way analysis of variance on the subject groups (bilingual, monolingual) and the data acquisition intervals (test, post 1, post 2) Measurement with EEG Simultaneous
8 9 10 32 33 34
11 12 13 14 35 36 37 38 revealed that, unlike the monolingual subjects, the bilingual subjects exhibited significant activation of the left DLPFC when evaluating
15 16 17 39 40 41 Channels presumed to a Japanese / Chinese isomorphic word presented with a picture showing the meaning specific to the non-target language (Chinese).
be positioned on
18 19 20 21 42 43 44 45 This result suggests that the left DLPFC activated to inhibit interference from the non-target language (Chinese). Unlike the left DLPFC,
Muzur et al.(2002) DLPFC (BA 45, 46, and 9)
22 23 24 46 47 48 the right DLPFC activated under a wide-range of conditions (Japanese-specific, Chinese-specific, does not exist in Japanese or Chinese)
Emitter Detector 1-48: Channels that require target language (Japanese) processing. Attention must be paid to the activation of the right DLPFC to determine whether Analysis Method NIRS Signal
Data Acquisition Intervals the subject understands the meaning in Japanese.
Japanese / Chinese isomorphic words were visually presented together with one of four types of pictures corresponding to a meaning Left Hemisphere fNIRS Data Right Hemisphere
that is Japanese-specific, Chinese-specific, shared in Japanese and Chinese, or does not exist in Japanese or Chinese. The bilingual and
monolingual subjects were asked to determine whether the picture represents the meaning in Japanese of the presented Japanese / Hit Correct rejection Hit Correct rejection
BL BL BL Japanese-specific Chinese-specific BL Inner Speech Investigating
Chinese isomorphic word. There are three data acquisition intervals: the "test" interval when the evaluation is performed, the "post JML Japanese-specific Chinese-specific JML JML JML
2
1" interval of hypothesized reduced searching for semantic information in the non-target language (L1, Chinese), and the "post 2" 2 1 4 1 8 5 2 9 6 10 3 7 4 1 8 5 2 9 6 10 3 7 2 1 1 28 25 32 29 26 33 30 27 34 31 28 25 32 29 26 33 30 27 34 31 2 1
interval of hypothesized concentration on the meaning in the target language (L2, Japanese). The Hb concentration changes in each Coxy Hb z score 0 11 18 15 22 12 19 16 23 13 20 17 24 14 21 11 18 15 22 12 19 16 23 13 20 17 24 14 21 Coxy Hb z score 0 Coxy Hb z score -1 0 35 42 39 46 36 43 40 47 37 44 41 48 38 45 35 42 39 46 36 43 40 47 37 44 41 48 38 45 Coxy Hb z score 0
interval were compared between the bilingual and monolingual subjects. -1 -2 Pre Fix Test Post1 Post2 -1 -2 Pre Fix Test Post1 Post2 -2 Pre Fix Test Post1 Post2 -1 -2 Pre Fix Test Post1 Post2
Shared Unshared Shared Unshared Functions Language Processing
Yes / No Responses to Four Meanings fNIRS Measurement Intervals
2 1 2 3 1 2 3 2 2 25 26 27 25 26 27 2
Japanese 1 11 4 8 12 5 9 13 6 10 14 7 11 4 15 8 12 5 16 9 13 6 10 17 14 7 1 1 28 35 32 39 29 36 33 40 30 37 34 41 31 38 28 35 32 39 29 36 33 40 30 37 34 41 31 38 1
ؿं (means "automobile" in Coxy Hb z score 0 18 15 22 19 16 23 20 17 24 21 18 22 19 23 20 24 21 Coxy Hb z score 0 Coxy Hb z score 0 42 46 43 47 44 48 45 42 46 43 47 44 48 45 Coxy Hb z score 0
Exists Does Not Exist + Chinese but "steam train" in -1 -1 -1 -1
Japanese) Steam train -2 -2 -2 -2
Shared Chinese-specific Pre Fix Test Post1 Post2 Pre Fix Test Post1 Post2 Pre Fix Test Post1 Post2 Pre Fix Test Post1 Post2
(e.g., Թઘ (means "hot spring" (e.g., ؿं (means "automobile" Reaction time
Exists in Japanese and in Chinese but "steam 1S 1S (approximately 5s) 6S 4S Research Mental Disorder
Chinese)) train" in Japanese)) (3S by 2 post periods) For semantic processing of the target language (L2) by bilingual subjects, fNIRS measurements clearly reveal that the left DLPFC is
pre fix test post 1 post 2 related to the reduced L1 activity in the early processing stage (post 1) and the right DLPFC is related to maintaining attention on L2 in
Chinese
Japanese-specific Unshared 0 1 2 3 4 the late processing stage (post 2).
(e.g., ؿं (means "automobile" (e.g., Թઘ (means "hot spring" Key response
Does Not in Chinese but "steam in Japanese and Baseline (Yes: known, No: unknown)
Exist train" in Japanese) ) Chinese) ) (Data supplied by: Hirofumi Saito, PhD, Graduate School of Information Science, Nagoya University)
Reference: Misato Oi, Hirofumi Saito, Hiroshi Ito and Paul L. Rumme. (2010). Shimadzu fNIRS Key References Regarding
Correct response Yes (known) No (unknown) "Semantic judgment of Chinese-Japanese bilinguals: a near-infraredspectroscopy study" NeuroReport 21(2): 127-131.
18 19