Page 9 - Clinical-MedicalSolution for Medical Chemistry
P. 9
Nexera UC UHPLC/SFC
Efficient Method Development using the UHPLC/SFC Switching System
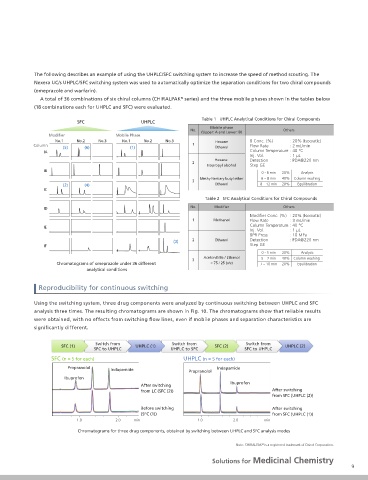
When considering separation conditions, using both UHPLC and SFC can help to optimize conditions further. The following describes an example of using the UHPLC/SFC switching system to increase the speed of method scouting. The
The Nexera UC/s UHPLC/SFC switching system provides the ability to use both UHPLC and SFC analysis modes in Nexera UC/s UHPLC/SFC switching system was used to automatically optimize the separation conditions for two chiral compounds
(omeprazole and warfarin).
a single system. The gure below shows a ow diagram for this system. The system was con gured by adding
A total of 36 combinations of six chiral columns (CHIRALPAK series) and the three mobile phases shown in the tables below
®
a supercritical carbon dioxide delivery unit and back pressure regulator unit to a standard UHPLC system. Both
(18 combinations each for UHPLC and SFC) were evaluated.
UHPLC and SFC analysis modes can be used by switching of delivery units (control mode ON or OFF) and
Table 1 UHPLC Analytical Conditions for Chiral Compounds
switching the pressure of the back pressure regulator. SFC UHPLC
Mobile phase
Sharing the solvent delivery unit (for pumping organic solvents), autosampler, column oven, and detector Modi er Mobile Phase No. (Upper: A and Lower: B) Others
for both SFC and UHPLC analysis minimizes space requirements and equipment cost and reduces equipment No.1 No.2 No.3 No.1 No.2 No.3 Hexane B Conc. (%) : 20% (Isocratic)
Column (5) (6) (1) 1 Ethanol Flow Rate : 2 mL/min
downtime. In addition, an existing UHPLC system can be upgraded to this system. IA Column Temperature : 40 °C
Inj. Vol. : 1 L
By using the mobile phase solvent 2 Hexane Detection : PDA@220 nm
Isopropyl alcohol Step GE
switching valve in combination with the IB 0 - 6 min 20% Analysis
column switching valve, mobile phase 3 Methyl tertiary butyl ether 6 – 8 min 40% Column washing
(2) (4) Ethanol 8 – 12 min 20% Equilibration
conditions can be changed automatically IC
and continuously for up to twelve Table 2 SFC Analytical Conditions for Chiral Compounds
columns to enable a wide variety of ID No. Modi er Others
Modifier Conc. (%) : 20% (Isocratic)
conditions, improving method 1 Methanol Flow Rate : 3 mL/min
Column Temperature : 40 °C
development ef ciency. IE Inj. Vol. : 1 L
BPR Press : 10 MPa
(3) 2 Ethanol Detection : PDA@220 nm
IF Step GE
0 - 5 min 20% Analysis
Acetonitrile / Ethanol 5 – 7 min 40% Column washing
3
Chromatograms of omeprazole under 36 different = 75 / 25 (v/v) 7 – 10 min 20% Equilibration
analytical conditions
Reproducibility for continuous switching
UHPLC column
Oven-A Using the switching system, three drug components were analyzed by continuous switching between UHPLC and SFC
SFC analysis three times. The resulting chromatograms are shown in Fig. 10. The chromatograms show that reliable results
Pump-A Column
Shutoff valve: (for CO2) switching valve Manifold were obtained, with no effects from switching ow lines, even if mobile phases and separation characteristics are
Open
signi cantly different.
Back pressure
Liquid CO2 regulator control: Switch from Switch from Switch from
cylinder Flow ON SFC (1) SFC to UHPLC UHPLC (1) UHPLC to SFC SFC (2) SFC to UHPLC UHPLC (2)
Pump-B switching valve Detector
SFC (n = 5 for each) UHPLC (n = 5 for each)
Autosampler Propranolol Indapamide Propranolol Indapamide
Ibuprofen
Mobile phase Ibuprofen
One UHPLC (organic solvent-based) After switching
pump added to from LC (SFC (2)) After switching
an SFC system from SFC (UHPLC (2))
Pump-C Before switching After switching
(SFC (1)) from SFC (UHPLC (1))
Oven-B 1.0 2.0 min 1.0 2.0 min
Mobile phase SFC Column
(water-based or buffer solution) Chromatograms for three drug components, obtained by switching between UHPLC and SFC analysis modes
LC
Nexera UC/s UHPLC/SFC switching system and ow line diagram (Equipment in green frame used for SFC) Note: CHIRALPAK ® is a registered trademark of Daicel Corporation.
Solutions for Medicinal Chemistry
8 9