Page 7 - Clinical-Medical Solution for Clinical Chemistry
P. 7
Application No.C123
News
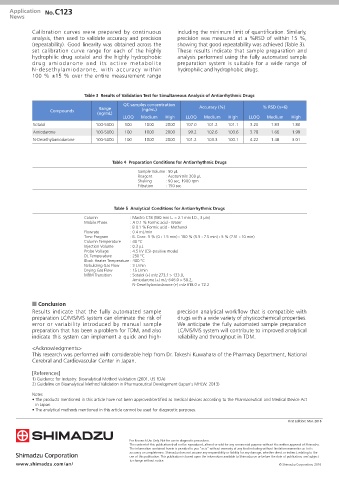
Calibration curves were prepared by continuous including the minimum limit of quantification. Similarly,
analysis, then used to validate accuracy and precision precision was measured at a %RSD of within 15 %,
(repeatability). Good linearity was obtained across the showing that good repeatability was achieved (Table 3).
set calibration curve range for each of the highly These results indicate that sample preparation and
hydrophilic drug sotalol and the highly hydrophobic analysis performed using the fully automated sample
drug amiodarone and its active metabolite preparation system is suitable for a wide range of
N-desethylamiodarone, with accuracy within hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs.
100 % ±15 % over the entire measurement range
Table 3 Results of Validation Test for Simultaneous Analysis of Antiarrhythmic Drugs
QC samples concentration
Range Accuracy (%) % RSD (n=6)
Compounds (ng/mL)
(ng/mL)
LLOQ Medium High LLOQ Medium High LLOQ Medium High
Sotalol 100-5000 100 1000 2000 107.0 101.2 101.1 3.20 1.83 1.80
Amiodarone 100-5000 100 1000 2000 99.2 102.6 100.6 3.78 1.66 1.99
N-Desethylamiodarone 100-5000 100 1000 2000 101.2 103.3 100.1 4.22 1.48 3.01
Table 4 Preparation Conditions for Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Sample Volume : 50 μL
Reagent : Acetonitrile 200 μL
Shaking : 90 sec, 1900 rpm
Filtration : 150 sec
Table 5 Analytical Conditions for Antiarrhythmic Drugs
Column : Mastro C18 (100 mm L. × 2.1 mm I.D., 3 μm)
Mobile Phase : A 0.1 % Formic acid - Water
: B 0.1 % Formic acid - Methanol
Flowrate : 0.4 mL/min
Time Program : B. Conc. 5 % (0 - 1.5 min) - 100 % (5.5 - 7.5 min) - 5 % (7.51 - 10 min)
Column Temperature : 40 °C
Injection Volume : 0.3 μL
Probe Voltage : 4.5 kV (ESI-positive mode)
DL Temperature : 250 °C
Block Heater Temperature : 400 °C
Nebulizing Gas Flow : 3 L/min
Drying Gas Flow : 15 L/min
MRM Transition : Sotalol (+) m/z 273.1 > 133.0,
Amiodarone (+) m/z 646.0 > 58.2,
N-Desethylamiodarone (+) m/z 618.0 > 72.2
n Conclusion
Results indicate that the fully automated sample precision analytical workflow that is compatible with
preparation LC/MS/MS system can eliminate the risk of drugs with a wide variety of physicochemical properties.
error or variability introduced by manual sample We anticipate the fully automated sample preparation
preparation that has been a problem for TDM, and also LC/MS/MS system will contribute to improved analytical
indicate this system can implement a quick and high- reliability and throughput in TDM.
<Acknowledgments>
This research was performed with considerable help from Dr. Takeshi Kuwahara of the Pharmacy Department, National
Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center in Japan.
[References]
1) Guidance for Industry: Bioanalytical Method Validation (2001, US FDA)
2) Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation in Pharmaceutical Development (Japan's MHLW, 2013)
Notes
• The products mentioned in this article have not been approved/certified as medical devices according to the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act
in Japan.
• The analytical methods mentioned in this article cannot be used for diagnostic purposes.
First Edition: Mar. 2016
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu.
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject
to change without notice.
www.shimadzu.com/an/ © Shimadzu Corporation, 2016