Page 66 - Clinical-Medical Solution for Clinical Chemistry
P. 66
Application No.C142$
News
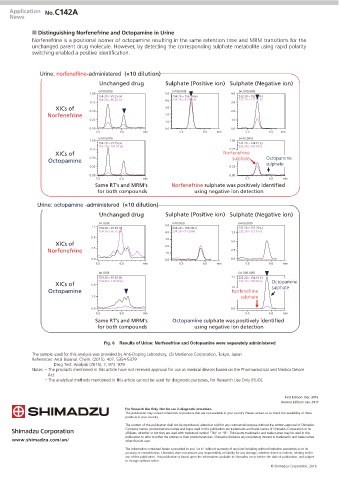
Q Distinguishing Norfenefrine and Octopamine in Urine
Norfenefrine is a positional isomer of octopamine resulting in the same retention time and MRM transitions for the
unchanged parent drug molecule. However, by detecting the corresponding sulphate metabolite using rapid polarity
switching enabled a positive identification.
Urine: norfenefrine-administered (×10 dilution)
Unchanged drug Sulphate (Positive ion) Sulphate (Negative ion)
(×100,000) (×100,000) (×1,000,000)
1.00 5.0 4.0
154.20 > 91.25 (+) 234.20 > 136.20 (+) 232.20 > 152.20 (-)
154.20 > 65.25 (+) 4.0 234.20 > 91.20 (+) 232.20 > 121.15 (-)
0.75 3.0
XICs of 0.50 3.0 2.0
Norfenefrine 2.0
0.25 1.0
1.0
0.00 0.0 0.0
5.5 6.0 min 5.5 6.0 min 5.5 6.0 min
(×100,000) (×100,000)
1.00 1.00
154.20 > 91.25 (+) 232.20 > 134.15 (-)
154.20 > 119.20 (+) 232.20 > 107.10 (-)
0.75 0.75
XICs of Norfenefrine
sulphate
0.50 0.50 Octopamine
Octopamine
sulphate
0.25 0.25
0.00 0.00
5.5 6.0 min 5.5 6.0 min
Same RT’s and MRM’s Norfenefrine sulphate was positively identified
for both compounds using negative ion detection
Urine: octopamine -administered (×10 dilution)
Unchanged drug Sulphate (Positive ion) Sulphate (Negative ion)
(×1,000) (×10,000) (×100,000)
7.5 5.0
154.20 > 91.25 (+) 234.20 > 136.20(+) 232.20 > 152.20 (-)
154.20 > 65.25 (+) 4.0 234.20 > 91.20(+) 7.5 232.20 > 121.15 (-)
5.0
3.0 5.0
XICs of 2.0
2.5
Norfenefrine 1.0 2.5
0.0 0.0 0.0
5.5 6.0 min 5.5 6.0 min 5.5 6.0 min
(×1,000) (×1,000,000)
154.20 > 91.25 (+) 1.5 232.20 > 134.15 (-)
154.20 > 119.20 (+) 232.20 > 107.10 (-) Octopamine
XICs of 5.0
1.0 sulphate
Octopamine Norfenefrine
2.5 0.5 sulphate
0.0 0.0
5.5 6.0 min 5.5 6.0 min
Same RT’s and MRM’s Octopamine sulphate was positively identified
for both compounds using negative ion detection
Fig. 6 Results of Urine: Norfenefrine and Octopamine were separately administered
The sample used for this analysis was provided by Anti-Doping Laboratory, LSI Medience Corporation, Tokyo, Japan
References: Anal Bioanal. Chem. (2015), 407, 5354-5379
Drug Test. Analysis (2015), 7, 973–979
Notes: ɾ The products mentioned in this article have not received approval for use as medical devices based on the Pharmaceutical and Medica Device
Act.
ɾ The analytical methods mentioned in this article cannot be used for diagnostic purposes, for Research Use Only (RUO).
First Edition: Dec. 2016
Second Edition: Jan. 2017
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedure.
This publication may contain references to products that are not available in your country. Please contact us to check the availability of these
products in your country.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu.
Company names, product/service names and logos used in this publication are trademarks and trade names of Shimadzu Corporation or its
affiliates, whether or not they are used with trademark symbol “TM” or “®”. Third-party trademarks and trade names may be used in this
publication to refer to either the entities or their products/services. Shimadzu disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names
www.shimadzu.com/an/ other than its own.
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject
to change without notice.
© Shimadzu Corporation, 2016