Page 25 - Shimadzu Journal vol.7 Issue1
P. 25
Environmental Analysis
⿏Preparation of Samples ⿏LCMS Analytical and Instrument Conditions
A surrogate spiking solution containing each isotopically-labelled PFAS The analytical and instrument conditions are listed in Table 3. Each
was added to all samples, including method blanks, duplicates, PFAS standard was injected and analyzed separately to ensure positive
laboratory control samples, matrix spikes and reporting limit checks. identification and maximum resolution. Upon collating the individual
The stock surrogate spiking solution was prepared at 20 µg/L in 95:5% retention time and optimized MRM parameters, the PFAS standard
(vol/vol) acetonitrile (ACN):water. Water samples (5 mL) were collected mixture (containing all PFAS compounds) was prepared and used for
in 15 mL PP/HDPE centrifuge vials. Also, the blank (containing 5 mL of subsequent analysis. All compound parameters, including precursor
reagent water) and laboratory control sample (containing the lowest ion, product ion and collision energies, were optimized bypassing the
calibration concentration for each PFAS) were prepared for the study. analytical column using LabSolutions software. At least two MRM
transitions were used.
The samples (5 mL) were diluted 1:1 with methanol and spiked with 40
µL of the surrogate spiking solution and vortexed for 2 minutes, Shimadzu UFMS™, possessing an ultra-fast acquisition rate of 555
resulting in a surrogate concentration of 80 ng/L in the diluted MRM/sec and a high polarity switching speed of 5 msec, is capable of
solution. The samples were filtered and acetic acid (10 µL) was added MRM transitions with a fast-enough cycle time to obtain high
to the filtrate to adjust the pH. The aliquots were transferred to the LC sensitivity with at least ten data points over a peak. The target
vials for injection and analysis by LC-MS/MS. compounds were identified by comparing the MRM transitions of the
sample to that of the standards. The target analytes were quantitated
using the quantifier MRM transitions (Table 4) of the target
compounds. Concentrations were calculated using LabSolutions
software to generate a linear regression. The point of origin was
excluded, and a fit weighting of 1/x was used to give more emphasis
to the lower concentrations.
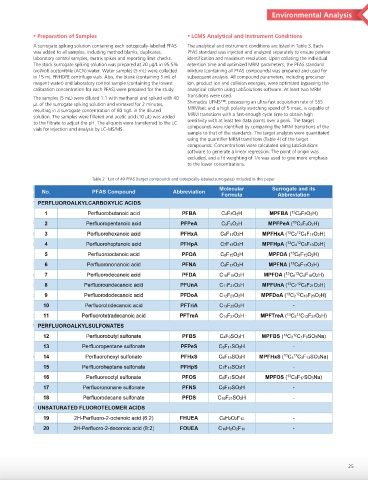
Table 2 List of 49 PFAS (target compounds and isotopically-labeled surrogates) included in this paper
25