Page 18 - Shimadzu Journal vol.7 Issue1
P. 18
Environmental Analysis
In addition, we noticed that as standards sat in the vials, loss of EPA and the International Standards Organization (ISO) have each
analyte occurred. We determined that the loss was not evaporation or recently completed an updated method, EPA 537.1 and ISO 21675,
precipitation, but that the higher molecular weight compounds tend both requiring SPE prior to LC-MS/MS. Table 7 compares these three
to either float up, or cling to the sides of the vial. Fig. 9 shows two PFAS methods.
chromatograms that demonstrate simply mixing the standard vial
returns the standards to their original response.
Before Vortex Same Vial After Vortex
Fig. 9 Chromatograms of Standards before and after mixing
Table 7 Comparison of three PFAS methods
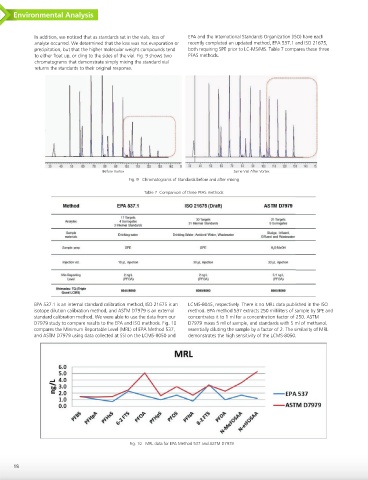
EPA 537.1 is an internal standard calibration method, ISO 21675 is an LCMS-8045, respectively. There is no MRL data published in the ISO
isotope dilution calibration method, and ASTM D7979 is an external method. EPA method 537 extracts 250 milliliters of sample by SPE and
standard calibration method. We were able to use the data from our concentrates it to 1 ml for a concentration factor of 250. ASTM
D7979 study to compare results to the EPA and ISO methods. Fig. 10 D7979 mixes 5 ml of sample, and standards with 5 ml of methanol,
compares the Minimum Reportable Level (MRL) of EPA Method 537, essentially diluting the sample by a factor of 2. The similarity of MRL
and ASTM D7979 using data collected at SSI on the LCMS-8050 and demonstrates the high sensitivity of the LCMS-8050.
Fig. 10 MRL data for EPA Method 537 and ASTM D7979
18