Page 5 - Shimadzu DUH-211/
P. 5
Materials and Applications
Thin Films Such as Vapor-Deposited Films and SiO2 (1 µm) Metallic Materials
Test force: 1 mN
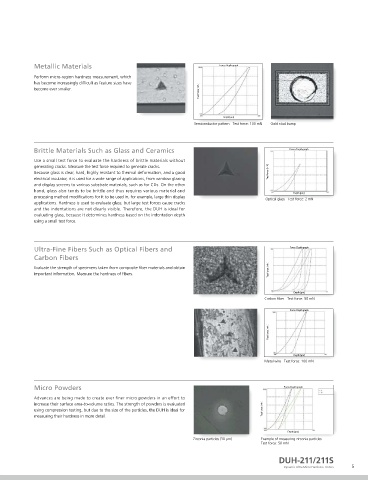
Semiconductor Materials, and Surface-Treated Perform micro-region hardness measurement, which
Layers Such as Ion-Implanted Layers and Nitride has become increasingly difficult as feature sizes have
Layers become ever smaller.
As film production technology improves and diversifies, it is becoming increasingly
important to evaluate the hardness of thin films and coatings on the surface of
materials. These include ion-implanted layers, DLC (diamond-like carbon) films,
vapor-deposited films produced by CVD (chemical vapor deposition), PVD (physical Plating layer on metal
vapor deposition) and alumite layer. By using an ultra micro test force to measure plate (Plating layer: Semiconductor pattern Test force: 100 mN Gold stud bump
Approx. 10 µm)
depths of less than one tenth of a film's thickness, the DUH tester makes it easy to
evaluate the hardness of only the film, without influence from underlying materials.
DLC Films Brittle Materials Such as Glass and Ceramics
DLC films offer properties such as high hardness, low friction coefficients, wear Use a small test force to evaluate the hardness of brittle materials without
resistance, electrical insulation, chemical resistance, and infrared light permeability, generating cracks. Measure the test force required to generate cracks.
and are widely used in tools, automotive parts, semiconductor manufacturing Because glass is clear, hard, highly resistant to thermal deformation, and a good
equipment parts, and household goods. Measuring the hardness of such films is electrical insulator, it is used for a wide range of applications, from window glazing
necessary for determining the optimal film manufacturing parameters and for and display screens to various substrate materials, such as for CDs. On the other
monitoring their quality, but creating large indentations is not possible. The DUH is hand, glass also tends to be brittle and thus requires various material and
perfect for these types of application, because it can evaluate hardness based on processing method modifications for it to be used in, for example, large thin display Optical glass Test force: 2 mN
the indentation depth using only a small test force. DLC Films Test force: 50 mN applications. Hardness is used to evaluate glass, but large test forces cause cracks
and the indentations are not clearly visible. Therefore, the DUH is ideal for
evaluating glass, because it determines hardness based on the indentation depth
Plastics using a small test force.
An important feature of engineering plastics is hardness. The DUH can measure the
hardness of even highly light-absorbent materials, which are difficult to measure
using conventional testers. Ultra-Fine Fibers Such as Optical Fibers and
Engineering plastics offer high strength, heat resistance, and other properties while
still providing the advantages of plastics in general such as superior plasticity and Carbon Fibers
ease of processing. As a result, they are commonly used for internal mechanical
parts (such as gears and bearings) in consumer electronic products. They provide Evaluate the strength of specimens taken from composite fiber materials and obtain
higher wear resistance, lighter weight, and lower cost than metal parts, and can be Thin film (30 µm) Test force: 5 mN important information. Measure the hardness of fibers.
mass produced, where hardness is used to improve performance and control
quality. However, the low reflectivity of plastics makes it difficult to measure the size
of indentations when using conventional hardness testers. In contrast, the DUH is
perfect for these applications, because it evaluates hardness based on the test force Carbon fiber Test force: 50 mN
applied and the resulting indentation depth.
Nylon Test force: 20 mN
Metal wire Test force: 100 mN
Rubbers and Elastomers
Because indentation depth is used to determine hardness, hardness can be
measured using a variety of test forces and the tester can even be used to evaluate Acrylic Test force: 20 mN
deterioration in material surfaces of materials. Micro Powders
Rubber provides a low elastic modulus, high elongation in response to small forces, Advances are being made to create ever finer micro powders in an effort to
and high repulsion. Consequently, its raw materials are often mixed with various increase their surface area-to-volume ratios. The strength of powders is evaluated
chemical ingredients to make a variety of products, such as tires, vibration using compression testing, but due to the size of the particles, the DUH is ideal for
absorbing rubber, and O-rings. Due to the harsh environments where such measuring their hardness in more detail.
products are typically used, in addition to evaluating durability, hardness is used to
also evaluate surface deterioration. However, conventional hardness testers cannot
evaluate the elastic characteristics of rubber because of the indentation after
testing. In contrast, the DUH measures both the test force and indentation depth, Due to elastic recovery, Silicone rubber Test force: 2 mN Zirconia particles (30 µm) Example of measuring zirconia particles
which makes it the perfect method for evaluating rubber, including its elasticity. no indentation remains Test force: 50 mN
DUH-211/211S
4 Dynamic Ultra Micro Hardness Testers 5