Page 8 - Shimadzu CFT-EX Series
P. 8
Supported by More Than 50 Years of
Technology and Know-How
For more than 50 years, the CFT series has been used in research and development, production process and quality management of various types of flowable
materials, including thermoplastic resins, thermosetting resins, toners and rubbers. Various applications are supported and extensive evaluations and analyses are
offered to meet the requirements of users.
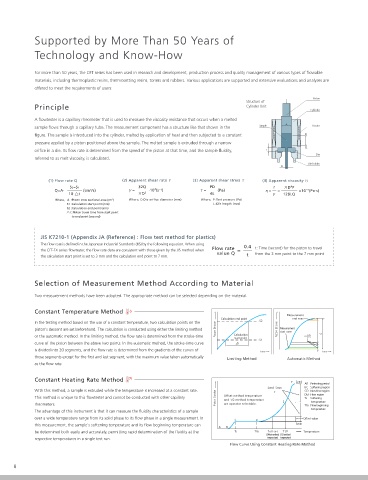
Piston
Structure of
Principle Cylinder Unit
Cylinder
A flowtester is a capillary rheometer that is used to measure the viscosity resistance that occurs when a melted
A
sample flows through a capillary tube. The measurement component has a structure like that shown in the Sample Heater
figure. The sample is introduced into the cylinder, melted by application of heat and then subjected to a constant S1
pressure applied by a piston positioned above the sample. The melted sample is extruded through a narrow
S2
orifice in a die. Its flow rate is determined from the speed of the piston at that time, and the sample fluidity, L
Die
referred to as melt viscosity, is calculated.
Die holder
D
(1) Flow rate Q (2) Apparent shear rate (3) Apparent shear stress (4) Apparent viscosity
4
S2−S1 32Q PD D P
3
−3
Q=A· (cm 3 /s) = ·10 (s −1 ) = (Pa) = = ×10 (Pa·s)
10· t D 3 4L 128LQ
Where, A :Piston cross sectional area (cm 2 ) Where, D:Die orifice diameter (mm) Where, P :Test pressure (Pa)
S1 :Calculation start point (mm) L :Die length (mm)
S2 :Calculation end point (mm)
t :Piston travel time from start point
to end point (second)
JIS K7210-1 (Appendix JA (Reference) : Flow test method for plastics)
The flow rate is defined in the Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) by the following equation. When using
Flow rate 0.4 t: Time (second) for the piston to travel
the CFT-EX series flowtester, the flow rate data are consistent with those given by the JIS method when =
value Q from the 3 mm point to the 7 mm point
the calculation start point is set to 3 mm and the calculation end point to 7 mm. t
Selection of Measurement Method According to Material
Two measurement methods have been adopted. The appropriate method can be selected depending on the material.
Constant Temperature Method
Measurement
Calculation end point end zone
In the testing method based on the use of a constant temperature, two calculation points on the S2
piston's descent are set beforehand. The calculation is conducted using either the limiting method Piston Stroke Piston Stroke Measurement
start zone
or the automatic method. In the limiting method, the flow rate is determined from the stroke-time Calculation S 20 S
start point
S1
curve of the piston between the above two points. In the automatic method, the stroke-time curve t
is divided into 20 segments, and the flow rate is determined from the gradients of the curves of Time Time
those segments except for the first and last segment, with the maximum value taken automatically
Limiting Method Automatic Method
as the flow rate.
Constant Heating Rate Method F Send
AB :Preheating period
Send−Smin BC :Softening region
With this method, a sample is extruded while the temperature is increased at a constant rate. 2 CD :Non-flow region
This method is unique to this flowtester and cannot be conducted with other capillary Piston Stroke Offset method temperature DEF:Flow region
Ts :Softening
and 1/2 method temperature
temperature
rheometers. are operator selectable. E Tfb :Flow beginning
temperature
The advantage of this instrument is that it can measure the fluidity characteristics of a sample
over a wide temperature range from its solid phase to its flow phase in a single measurement. In Offset value
C D
this measurement, the sample's softening temperature and its flow beginning temperature can Smin
A B
be determined both easily and accurately, permitting rapid determination of the fluidity at the Ts Tfb Toffset T1/2 Temperature
(Offset method (1/2 method
respective temperatures in a single test run. temperature) temperature)
Flow Curve Using Constant Heating Rate Method
8