Page 6 - Shimadzu AIRsight
P. 6
AIRsight
Applications
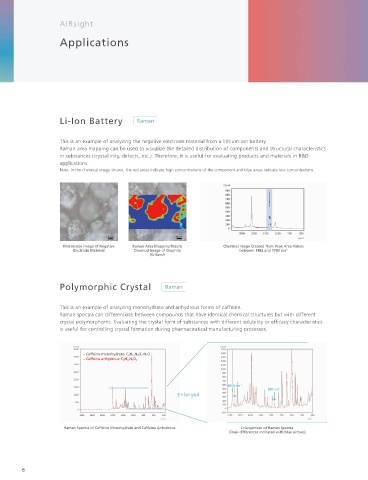
Li-Ion Battery Multilayer Film Microscope Image of
Multilayer Film Cross Section Interior
This is an example of analyzing the negative electrode material from a lithium-ion battery. This is an example of analyzing a multilayer lm. Surface layer
Raman area mapping can be used to visualize the detailed distribution of components and structural characteristics The distribution of each component can be visualized by using infrared
in substances (crystallinity, defects, etc.). Therefore, it is useful for evaluating products and materials in R&D and Raman area mapping to analyze a cut cross section from the lm.
applications.
Note: In the chemical image shown, the red areas indicate high concentrations of the component and blue areas indicate low concentrations.
Infrared Area Mapping Results Chemical Image Created from Peak Raman Area Mapping Results Chemical Image Created from Peak
Chemical Image of Phthalate Esters Areas between 1551 and 1624 cm -1 Chemical Image of Titanium Area Values between 345 and 508 cm -1
Microscope Image of Negative Raman Area Mapping Results Chemical Image Created from Peak Area Values Oxide (Rutile)
Electrode Material Chemical Image of Graphite between 1482 and 1703 cm -1
(G-Band)
Polymorphic Crystal Automotive Paint Coating
This is an example of analyzing monohydrate and anhydrous forms of caffeine. This is an example of analyzing an automotive paint coating. Samples with characteristics that make it dif cult to
Raman spectra can differentiate between compounds that have identical chemical structures but with different cut a cross section can be evaluated by analyzing the component distribution in the depth direction by Raman
crystal polymorphisms. Evaluating the crystal form of substances with different solubility or ef cacy characteristics spectroscopy and evaluating the degradation status or other criteria from the surface.
is useful for controlling crystal formation during pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. A separate mapping program (P/N 206-35093-41) is required.
X X
– Caffeine monohydrate: C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2 ·H 2 O Y Z
– Caffeine anhydrous: C 8 H 10 N 4 O 2
1656 cm -1 -1
1656 cm
887 cm -1 -1
887 cm
Shiny Exterior Microscope Image of Automotive Raman Depth (Line) Mapping Chemical Image Created from
Paint Coating Results Peak Area Values between 1383
(Blue circles: Line axis in X-direction) Chemical Image of Acrylic Resin and 1510 cm -1
Raman Spectra of Caffeine Monohydrate and Caffeine Anhydrous Enlargement of Raman Spectra
(Peak differences indicated with blue arrows)
6 7