Page 5 - Shimadzu AIRsight
P. 5
AIRsight
Applications
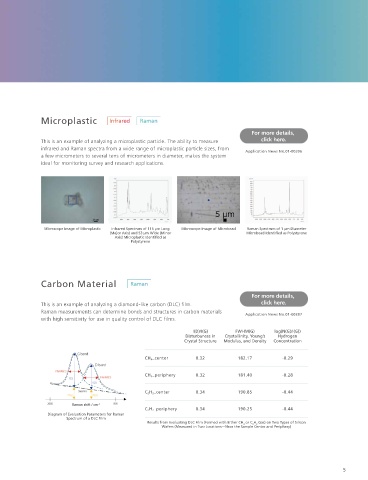
Contaminant Microplastic
For more details, For more details,
This is an example of analyzing a contaminant (simulated sample) attached to click here. This is an example of analyzing a microplastic particle. The ability to measure click here.
the surface of a pharmaceutical tablet. Obtaining both infrared and Raman infrared and Raman spectra from a wide range of microplastic particle sizes, from
Application News No.01-00394 Application News No.01-00396
measurements from the same spot increases the accuracy of qualitative analysis a few micrometers to several tens of micrometers in diameter, makes the system
to help identify the cause of contaminants. ideal for monitoring survey and research applications.
– Normal area – Normal area
– Contaminant – Contaminant
adhesion area adhesion area
Microscope Image of Microplastic Infrared Spectrum of 115 µm Long Microscope Image of Microbead Raman Spectrum of 1 µm Diameter
(Major Axis) and 53 µm Wide (Minor Microbead Identi ed as Polystyrene
Axis) Microplastic Identi ed as
Polystyrene
Microscope Image of Contaminant Infrared Spectra of Normal and Contaminant Raman Spectra of Normal and Contaminant
Adhesion Areas with Normal Area Identi ed as Adhesion Areas with Contaminant Identi ed as
Mannitol Iron Oxide
Pigment Carbon Material
For more details, For more details,
This is an example of analyzing pigment applied to wood. click here. This is an example of analyzing a diamond-like carbon (DLC) lm. click here.
Because AIRsight microscopes can measure trace quantities, they are especially Application News No.01-00395 Raman measurements can determine bonds and structures in carbon materials Application News No.01-00397
useful for measuring precious samples with historical value. with high sensitivity for use in quality control of DLC lms.
I(D)/I(G) FWHM(G) log(N(G)/I(G))
Disturbances in Crystallinity, Young’s Hydrogen
– Infrared spectrum Crystal Structure Modulus, and Density Concentration
– Raman spectrum
CH 4 _center 0.32 182.17 -0.29
CH 4 _periphery 0.32 181.40 -0.28
C 2 H 2 _center 0.34 190.85 -0.44
Appearance of Pigment Applied to Wood Microscope Image of Pigment Applied to a Infrared and Raman Spectra of Pigment with
Wood Surface BaSO 4 Identi ed from the IR Spectrum and Pb 3 O 4 Raman shift / cm -1
from the Raman Spectrum C 2 H 2 _periphery 0.34 190.25 -0.44
Diagram of Evaluation Parameters for Raman
Spectrum of a DLC Film
Results from Evaluating DLC Film (Formed with Either CH 4 or C 2 H 2 Gas) on Two Types of Silicon
Wafers (Measured in Two Locations—Near the Sample Center and Periphery)
4 5