Page 7 - MUP-3100
P. 7
Processes 24 Culture Supernatant Samples Possible to Verify the Profiling of Glycosylation from Antibodies
Reliably in 6 Hours in Culture Supernatant) & Towards Achieving an Efficient
Workflow for Optimizing Culture Conditions
[Introduction to the applications of Auto-EZGlyco mAb-N Kit for
Complicated procedures can be automatically processed in 6 hours SHIMADZU (utilizing MUP-3100 for preprocessing]
(the MUP-3100 + the antibody N-glycan analysis kit)
In the results shown below, antibody standard samples were added to culture supernatants from CHO-K1 cells, which are often
used as production host cells for antibody preparations, and CHL-YN cells, which are antibody production host cells derived from
Conventional methods require complex operations to cut out glycans from antibody samples in the culture supernatant. The Chinese hamster lungs established in recent years. The MUP-3100 and the kit was used to recover the N-glycan of antibodies, and
traditional method requires more than two days for preprocessing. When using the MUP-3100 and the antibody N-glycan the recovery rate of the N-glycan was found to be equivalent regardless of the type of matrix. When pretreatment is performed
analysis kit in combination, however, 24 samples can be preprocessed in six hours. using the MUP-3100 and the kit, glycan profiles can be confirmed with no impact from the impurities in the culture supernatants.
Glycan profiling, including the type and quantity of glycans, can be performed by analysis of 2-AB labeled glycans using an HPLC
fluorescence detector. The Shim-pack GIST-HP Amide [Metal Free] column is effective for separating out impurities and glycans
contained in antibody preparations and culture supernatants.
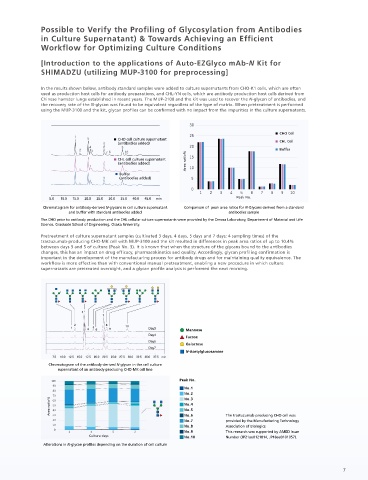
CHO Cell
CHO cell culture supernatant
(antibodies added) CHL Cell
mV Buffer
Area ratio%
CHL cell culture supernatant
(antibodies added)
Buffer
(antibodies added)
MUP-3100
Peak No.
Chromatogram for antibody-derived N-glycans in cell culture supernatant Comparison of peak area ratios for N-Glycans derived from a standard
and buffer with standard antibodies added antibodies sample
The CHO prior to antibody production and the CHL cellular culture supernatants were provided by the Omasa Laboratory, Department of Material and Life
Science, Graduate School of Engineering, Osaka University.
HPLC chromatogram for standard samples of antibody-derived glycans (from human serum IgG) with
Shim-pack GIST-HP Amide [Metal Free] column
Pretreatment of culture supernatant samples (cultivated 3 days, 4 days, 5 days and 7 days; 4 sampling times) of the
trastuzumab-producing CHO-MK cell with MUP-3100 and the kit resulted in differences in peak area ratios of up to 10.4%
High performance Liquid chromatograph
liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer between days 3 and 5 of culture (Peak No. 3). It is known that when the structure of the glycans bound to the antibodies
(HPLC) (LC-MS) changes, this has an impact on drug efficacy, pharmacokinetics and quality. Accordingly, glycan profiling confirmation is
important in the development of the manufacturing process for antibody drugs and for maintaining quality equivalence. The
workflow is more effective than with conventional manual pretreatment, enabling a new procedure in which culture
supernatants are pretreated overnight, and a glycan profile analysis is performed the next morning.
Allowing simultaneous processing of up to 24 samples
(MUP-3100 + antibody N-glycan analysis kit)
The MUP-3100 can process 24 samples at a time. Even with simultaneous processing of other samples, the area ratio of each
peak remains stable regardless of peak intensity, yielding data equivalent to that obtained when using the kit manually.
Mannose
Fucose
Galactose
N-Acetylglucosamine
Chromatogram of the antibody-derived N-glycan in the cell culture
supernatant of an antibody-producing CHO-MK cell line
Peak No.
No.1
No.2
No.3
Area ratio% No.4
No.5
Comparison of peak area ratios for the N-Glycan (identical samples) derived from IgG in human serum No.6 The trastuzumab-producing CHO cell was
No.7 provided by the Manufacturing Technology
No.8 Association of Biologics.
No.1 No.2 No.3 No.4 No.5 No.6 Mannose Sialic Acid
No.2
No.2
No.2
No.7 No.8 No.9 No.10 No.11 No.12 No.9 This research was supported by AMED Issue
No.8
No.8
No.8
Fucose N-Acetylglucosamine Culture days
No.14
No.13 No.14 No.15 No.16 No.17 No.18 No.10 Number (JP21ae0121014, JP18ae0101057).
No.14
No.14
No.19 No.20 No.21 No.22 No.23 No.24 Galactose Alterations in N-glycan profiles depending on the duration of cell culture
No.20
No.20
No.20
6 7