Page 7 - Guide to Lithium-ion Battery Solutions
P. 7
Material Testing
Compression test of various materials that construct a Lithium-ion Battery Purpose Samples
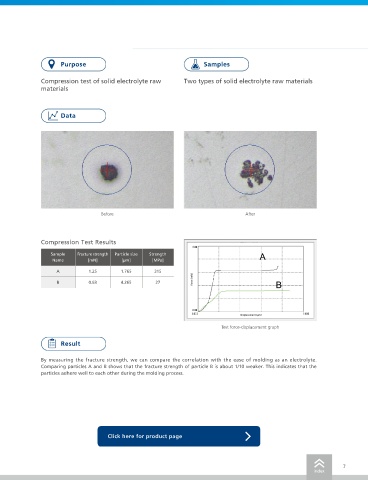
Compression test of solid electrolyte raw Two types of solid electrolyte raw materials
materials
Micro Compression Tester
MCT Series
Data
• Consideration of conditions for battery packaging and
restraint pressure
• Examination of manufacturing process conditions (change in
strength during heating)
Inner structural materials of a Lithium-ion Battery are subjected to external force during production processes and to
pressure during use. Therefore, evaluating the strength of each structural material is important to maintain consistent
quality. Below are the results of compression tests performed on Lithium-ion Battery materials using the Micro
Compression Testing Machine.
Before After
Purpose Samples
Compression test of positive electrode active Two types of positive electrode active Compression Test Results
materials materials
Sample Fracture strength Particle size Strength
Name [mN] [µm] [MPa]
Data
A 1.25 1.765 315
Force (mN)
Compression Test Results B 0.63 4.265 27
Sample Fracture strength Particle size Strength
Name [mN] [µm] [MPa]
Force (mN)
1.67 13.0 7.79
LiMn 2 O 4 Displacement (μm)
16.23 13.3 72.75
LiCoO 2
Test force-displacement graph
Result
Displacement (μm)
By measuring the fracture strength, we can compare the correlation with the ease of molding as an electrolyte.
Test force-displacement graph
Comparing particles A and B shows that the fracture strength of particle B is about 1/10 weaker. This indicates that the
particles adhere well to each other during the molding process.
Result
The force is on the vertical axis, the displacement is on the horizontal axis, and fracture occurs at the inflection point
where the displacement becomes horizontal. The fracture strength of the lithium cobalt oxide LiCoO 2 particle was
measured to be 72.75 MPa compared to 7.79 MPa for the lithium manganese oxide, LiMn 2 O 4 .
Click here for product page Click here for product page
6 7
index index