Page 8 - LifeScience Solution for Lipid and Lipidome
P. 8
Lipid Analysis Using Supercritical Fluid Technology
Data Subcutaneous Tissue Mass Imaging of
Supercritical fluids are fluids that are above their critical point. They have
properties of both gases and liquids, such as low viscosity, high diffusivity, and
Bioactive lipids with a lysophospholipid skeleton are referred to as lysophospholipid mediators and are attracting attention as high solubility. Generally, carbon dioxide is used for supercritical fluids.
second-generation bioactive lipids. One typical lysophospholipid mediator is sphingosine-1-phosphate. Fingolimod, a drug released Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) uses a supercritical fluid to extract Analysis of
in 2011 for treating multiple sclerosis and used as an active ingredient of pharmaceuticals, is presumed to function as a components, which offers the advantage of easier solvent removal than Comprehensive
sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonist. Lysophosphatidic acid is a lysophospholipid with an extremely simple conventional solvent extraction methods. Supercritical fluid chromatography Glycerophospholipids
phosphate-glycerol-fatty acid structure, but an extremely diverse range of its effects have been reported. These include cell uses supercritical fluid as a mobile phase. Due to properties of supercritical
proliferation, cell locomotion, platelet coagulation, and smooth muscle contraction. fluids, it achieves higher speed and higher separation for simultaneous analysis.
Peaks Technology Supercritical Fluid
1. Phosphatidyl Choline Lipid Analysis Using
2. Lyso Phosphatidyl Choline
3. Phosphatidyl Ethanolamine
4. Lyso Phosphatidyl Ethanolamine Dried Blood Spots
5. Phosphatidyl Glycerol
6. Phosphatidyl Inositol
Supercritical Fluid Technology Analysis of
Nexera UC improves the analytical workflow by utilizing a completely new separation Unified Chromatography Glycerophospholipids
technology, Unified Chromatography, which unites sample separation, analysis with
various separation modes, and high-sensitivity detection.
SFC
The Nexera UC on-line SFE-SFC system is a revolutionary system that combines
supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) with supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC). By LC
automating the process of target compound extraction from solid samples and analysis, GC Blood Serum
0 2.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 min the system offers a variety of new solutions. Mediators in Human Analysis of Lipid
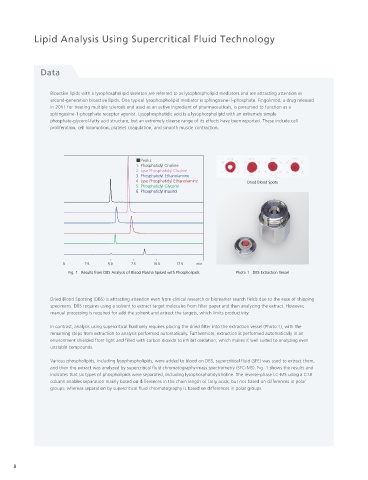
Fig. 1 Results from DBS Analysis of Blood Plasma Spiked with Phospholipids Photo 1 DBS Extraction Vessel
• Automates process from target component extraction to analysis
Automatically extracts components from solid samples using a supercritical fluid and then analyzes them on-line, without any
intervention.
Dried Blood Spotting (DBS) is attracting attention even from clinical research or biomarker search fields due to the ease of shipping
• Analyzes unstable compounds without pretreatment
specimens. DBS requires using a solvent to extract target molecules from filter paper and then analyzing the extract. However,
Extraction is performed automatically in an environment shielded from light and that inhibits oxidation, which makes it possible
manual processing is required for add the solvent and extract the targets, which limits productivity. of Glycolipids
to analyze even unstable compounds that were previously decomposed in the pretreatment stage. Structural Analysis
In contrast, analysis using supercritical fluid only requires placing the dried filter into the extraction vessel (Photo 1), with the • Achieves the ultimate in high speed, high separation, and high sensitivity
remaining steps from extraction to analysis performed automatically. Furthermore, extraction is performed automatically in an Using supercritical fluid provides high-separation, high-sensitivity analysis that allows shorter analysis times for simultaneous
environment shielded from light and filled with carbon dioxide to inhibit oxidation, which makes it well suited to analyzing even analysis of multiple components.
unstable compounds.
Various phospholipids, including lysophospholipids, were added to blood on DBS, supercritical fluid (SFE) was used to extract them, Analysis of Fatty Acid
and then the extract was analyzed by supercritical fluid chromatography-mass spectrometry (SFC-MS). Fig. 1 shows the results and Content of Human ES Cells Composition in Overall Lipid
indicates that six types of phospholipids were separated, including lysophosphatidylcholine. The reverse-phase LC-MS using a C18
column enables separation mainly based on differences in the chain length of fatty acids, but not based on differences in polar
groups, whereas separation by supercritical fluid chromatography is based on differences in polar groups.
Supercritical Fluid Extraction/Chromatograph System Esters by GC Acid Methyl Analysis of Fatty
Nexera UC
Reference: Nexera UC brochure (C190-E185)
8 9