Page 19 - Food&Beverages Solution Palm Oil
P. 19
Gas Chromatograph Mass Spectrometer (GCMS) Gas Chromatograph Mass Spectrometer (GCMS)
Trans Unsaturated Fatty Acid Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
Trans fat, or trans-unsaturated fatty acids, are a type of unsaturated fat that occurs in small amounts in nature, but became widely Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are organic chemicals that have a high vapor pressure at ordinary room temperature. Their high vapor
produced industrially from vegetable fats for use in margarine, snack food, packaged baked goods, and fried fast food. Trans fat has been pressure results from a low boiling point, which causes large numbers of molecules to evaporate or sublimate from the liquid or solid form
shown to consistently be associated, in an intake-dependent way, with increased risk of coronary artery disease. In food production, the of the compound and enter the surrounding air, a trait known as volatility. VOCs are numerous, varied, and ubiquitous. They include both
goal is to decrease the number of double bonds and increase the amount of hydrogen in the fatty acid. This changes the consistency of human-made and naturally occurring chemical compounds. Some VOCs are dangerous to human health or cause harm to the environment.
the fatty acid and makes it less prone to rancidity. Production of trans fatty acids is therefore an undesirable side effect of partial Harmful VOCs typically are not acutely toxic, but have compounding long-term health effects. Because the concentrations are usually low
hydrogenation. Trans fat levels may be measured. Figure 1 shows the results from GC × GC-MS analysis of methyl esterified lipids and the symptoms slow to develop, research into VOCs and their effects is difficult.
extracted from commercial butter by the Folch method.
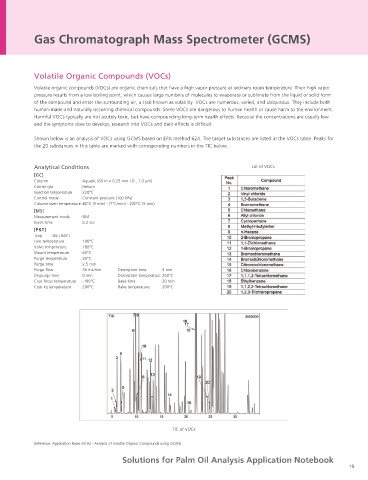
Shown below is an analysis of VOCs using GCMS based on EPA method 624. The target substances are listed in the VOCs table. Peaks for
Analytical Conditions the 20 substances in this table are marked with corresponding numbers in the TIC below.
GC×GC modulator : ZX1-GC×GC modulator
GC-MS : GCMS-QP2010 Ultra
[GC×GC] [MS] Analytical Conditions List of VOCs
Column :1st DB-1 (30 m × 0.25 mm I.D., 0.25 µm) Ion source temperature :200°C [GC]
2nd Rtx-WAX (2.5 m × 0.1 mm I.D., 0.1 µm) Interface temperature :240°C Column :Aquatic (60 m × 0.25 mm I.D., 1.0 µm)
Injection volume :1.0 µL Solvent elution time :15.5 min Carrier gas :Helium
Injection mode :Split (split ratio, 100) Data sampling time :16 min to 80 min Injection temperature :220°C
Vaporization chamber temperature :250°C Measurement mode :Scan (m/z 45 to 330) Control mode :Constant pressure (100 kPa)
Column oven temperature :40°C (2 min) - (30°C/min) - 160°C- (2°C/min) - 300°C (5 min) Event time :0.02 sec Column oven temperature :40°C (5 min) - (7°C/min) - 220°C (5 min)
Control mode :Constant pressure (150 kPa) [MS]
Modulation time :8 sec Measurement mode :SIM
Hot pulse time :0.5 sec (325°C) Event time :0.2 sec
[P&T]
Trap :GL-TRAP1
Line temperature :180°C
Valve temperature :180°C
Mount temperature :60°C
Purge temperature :35°C
Purge time :2.5 min
Purge flow :30 mL/min Desorption time :3 min
Drypurge time :0 min Desorption temperature :200°C
Cryo focus temperature :-190°C Bake time :20 min
Cryo Inj temperature :200°C Bake temperature :200°C
2-Dimensional Image of GC×GC-MS Analysis Results for Butter
TIC of VOCs
Reference: Application Data Sheet No. 27 - Analysis of Fatty Acids in Butter Using GC×GC-MS Reference: Application News M193 - Analysis of Volatile Organic Compounds using GC/MS
Solutions for Palm Oil Analysis Application Notebook
18 19