Page 27 - Food&Beverages Beer
P. 27
Brewing Chemistry Analysis – Packaging Testing for Beer
N-Nitrosamines
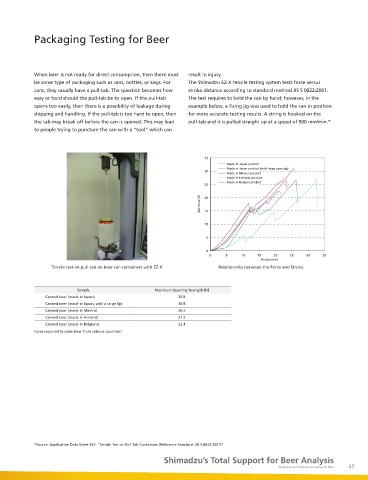
Most N-nitrosamines are known to be carcinogenic and amount of nitrosamines in beer must be controlled to the When beer is not ready for direct consumption, then there must result in injury.
mutagenic. Consumption of nitrosamines, e.g., acceptable levels, typically at 0.2 ~ 5.0 ppb depending on the be some type of packaging such as cans, bottles, or kegs. For The Shimadzu EZ-X tensile testing system tests force versus
N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA), was reported to be a cause of country. The main N-nitrosamine that is monitored in malt and cans, they usually have a pull-tab. The question becomes how stroke distance according to standard method JIS S 0022:2001.
gastric cancer, liver cancer, glioma and blood disorder. beer is NDMA. easy or hard should the pull-tab be to open. If the pull-tab The test requires to hold the can by hand; however, in the
N-nitrosamines can be formed by a reaction between amine and Shown is a GC-MS/MS method using Multiple Reaction opens too easily, then there is a possibility of leakage during example below, a fixing jig was used to hold the can in position
nitrite under heating conditions in food processing. They have Monitoring (MRM) mode for simultaneous detection and shipping and handling. If the pull-tab is too hard to open, then for more accurate testing results. A string is hooked on the
been found in malt-derived beverages like beer at trace levels. quantification of six N-nitrosamines, including NDMA, for the tab may break off before the can is opened. This may lead pull-tab and it is pulled straight up at a speed of 500 mm/min.*
The presence of NDMA in malt and beer was first reported in enhanced selectivity and sensitivity from the potential matrix to people trying to puncture the can with a “tool” which can
1974. Its concentration in malt depends on the drying interferences in beer samples*.
techniques used. According to US and EU regulations, the
35
Made-in-Japan product
(x100) (x100) (x100) 30 Made-in-Japan product (with large opening)
74.10>42.00 102.10>85.10 3.0 158.20>99.10 Made-in-Mexico product
2.25 74.10>30.00 102.10>56.00 158.20>141.20 Made-in-Holland product
2.5
2.00 2.5 25 Made-in-Belgian product
1.75 2.0
2.0
1.50
1.5 20
1.25 1.5 Test force [N]
1.00 1.0
1.0 15
0.75
0.5
6.7 6.8 7.3 7.4 9.4 9.5
NDMA NDEA NDBA 10
(x100) (x100) (x100)
1.3 114.10>97.10 100.10>70.00 116.10>86.00 5
100.10>55.00
116.10>56.00
6.0 4.0
1.2
3.5
1.1 0
5.0 3.0
1.0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35
0.9 4.0 2.5 Stroke [mm]
0.8 2.0 Tensile test on pull-tab on beer can containers with EZ-X Relationship between the Force and Stroke
0.7 3.0 1.5
0.6 1.0
0.5 2.0 0.5
9.7 9.8 9.9 10.0 10.1 10.2
NPIP NPYP NMOP Sample Maximum Opening Strength [N]
MRM transitions of six N-Nitrosamines at Shimadzu GCMS-TQ8040 triple Canned beer (made in Japan) 26.8
0.1 ppb in Beer by GC-MS/MS quadrupole mass Spectrometer Canned beer (made in Japan, with a large lip) 30.8
Canned beer (made in Mexico) 26.5
Canned beer (made in Holland) 27.2
Canned beer (made in Belgium) 22.4
Force required to open beer from various countries*
*ASMS 2013 Poster TP738: “Method Development for Trace Level Detection of N-Nitrosamines in Beer by GC-MS/MS” *Source: Application Data Sheet #25: “Tensile Test on Pull-Tab Containers (Reference Standard: JIS S 0022:2001)”
Shimadzu’s Total Support for Beer Analysis
26 Analytical and Testing Instruments for Beer 27