Page 6 - Shimadzu Journal vol.5 Issue1
P. 6
Glycan Analysis
Analysis of Glycan Structures Using Chemical Labeling and
MALDI MSn Mass Spectrometry
2
3
Yan Li , Scott A. Kuzdzal , Daniel W. Chan , Hui Zheng 3
1
1ɹBiophysics of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China 2ɹShimadzu Scientific Instruments, Columbia, MD, USA
3ɹJohns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD, USA
Abstract
Background:
Glycans play important roles in the function of glycoproteins in human body. Currently, the detail structure analysis is challenging due to the
time-consuming and labor-intensive glycan analysis procedure, which usually includes multi-step sequential treatments, HPLC or electrophoreses
purification, and mass spectrometry analysis.
Methods:
n
In this study, an AXIMA-Resonance™ was used to generate MALDI-IT-TOF- MS spectra for the analysis of the glycan sequences without
multistep separation or enzymatic treatment. We used MS mass spectrometry to monitor the oxidization of glycans.
n
Results:
n
n
The MS data showed that mild oxidation condition specifically oxidized sialic acid. Combining the carbohydrate oxidation reaction and MS
analysis, we were able to monitoring the oxidization reaction for sialylation and linkages of oligosaccharides.
1. Methods and Results
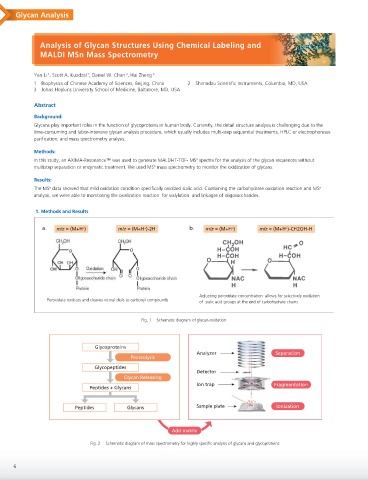
a. m/z = (M+H ) m/z = (M+H )-2H b. m/z = (M+H ) m/z = (M+H )-CH2OH-H
+
+
+
+
Adjusting peroxidate concentration allows for selectively oxidation
Peroxidate oxidizes and cleaves vicinal diols to carbonyl compounds
of sialic acid groups at the end of carbohydrate chains
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of glycan oxidation
Glycoproteins
Analyzer Separation
Proteolysis
Glycopeptides
Detector
Glycan Releasing
Ion trap Fragmentation
Peptides + Glycans
Peptides Glycans Sample plate Ionization
Add matrix
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of mass spectrometry for highly specific analysis of glycans and glycoproteins
6