Page 8 - Shimadzu Journal vol.2 Issue1
P. 8
Human Health
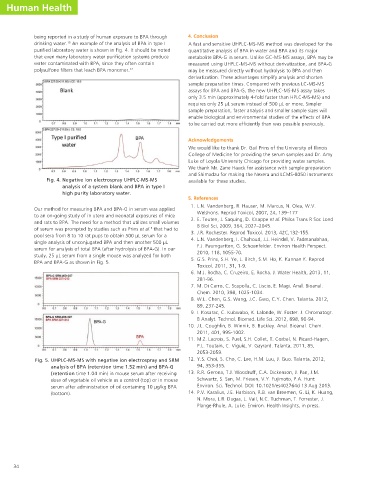
being reported in a study of human exposure to BPA through 4. Conclusion
drinking water. An example of the analysis of BPA in type I A fast and sensitive UHPLC-MS-MS method was developed for the
15
purified laboratory water is shown in Fig. 4. It should be noted quantitative analysis of BPA in water and BPA and its major
that even many laboratory water purification systems produce metabolite BPA-G in serum. Unlike GC-MS-MS assays, BPA may be
water contaminated with BPA, since they often contain measured using UHPLC-MS-MS without derivatization, and BPA-G
polysulfone filters that leach BPA monomer. 12 may be measured directly without hydrolysis to BPA and then
derivatization. These advantages simplify analysis and shorten
sample preparation times. Compared with previous LC-MS-MS
assays for BPA and BPA-G, the new UHPLC-MS-MS assay takes
only 3.5 min (approximately 4-fold faster than HPLC-MS-MS) and
requires only 25 µL serum instead of 500 µL or more. Simpler
sample preparation, faster analysis and smaller sample sizes will
enable biological and environmental studies of the effects of BPA
to be carried out more efficiently than was possible previously.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Dr. Gail Prins of the University of Illinois
College of Medicine for providing the serum samples and Dr. Amy
Luke of Loyola University Chicago for providing water samples.
We thank Mr. Zane Hauck for assistance with sample preparation
and Shimadzu for making the Nexera and LCMS-8050 instruments
Fig. 4. Negative ion electrospray UHPLC-MS-MS available for these studies.
analysis of a system blank and BPA in type I
high purity laboratory water.
5. References
1. L.N. Vandenberg, R. Hauser, M. Marcus, N. Olea, W.V.
Our method for measuring BPA and BPA-G in serum was applied
to an on-going study of in utero and neonatal exposures of mice Welshons. Reprod Toxicol, 2007, 24, 139–177
and rats to BPA. The need for a method that utilizes small volumes 2. E. Teuten, J. Saquing, D. Knappe et al. Philos Trans R Soc Lond
5
of serum was prompted by studies such as Prins et al. that had to B Biol Sci, 2009, 364, 2027–2045.
pool sera from 8 to 10 rat pups to obtain 500 µL serum for a 3. J.R. Rochester. Reprod Toxicol. 2013, 42C,132-155.
single analysis of unconjugated BPA and then another 500 µL 4. L.N. Vandenberg, I. Chahoud, J.J. Heindel, V. Padmanabhan,
serum for analysis of total BPA (after hydrolysis of BPA-G). In our F.J. Paumgartten, G. Schoenfelder. Environ Health Perspect.
study, 25 µL serum from a single mouse was analyzed for both 2010, 118, 1055-70.
BPA and BPA-G as shown in Fig. 5. 5. G.S. Prins, S.H. Ye, L. Birch, S.M. Ho, K. Kannan K. Reprod
Toxicol. 2011, 31, 1-9.
6. M.J. Rocha, C. Cruzeiro, E. Rocha. J. Water Health, 2013, 11,
281-96.
7. M. Di Carro, C. Scapolla, C. Liscio, E. Magi. Anal. Bioanal.
Chem. 2010, 398, 1025-1034.
8. W.L. Chen, G.S. Wang, J.C. Gwo, C.Y. Chen. Talanta. 2012,
89, 237-245.
9. I. Kosarac, C. Kubwabo, K. Lalonde, W. Foster. J. Chromatogr.
B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 898, 90-94.
10. J.L. Coughlin, B. Winnik, B. Buckley. Anal. Bioanal. Chem.
2011, 401, 995-1002.
11. M.Z. Lacroix, S. Puel, S.H. Collet, T. Corbel, N. Picard-Hagen,
P.L. Toutain, C. Viguié, V. Gayrard. Talanta, 2011, 85,
2053-2059.
The lower limit of quantitation for BPA in water was 0.01 ng/mL, Fig. 5. UHPLC-MS-MS with negative ion electrospray and SRM 12. Y.S. Choi, S. Cho, C. Lee, H.M. Luu, J. Guo. Talanta, 2012,
and the lower limits of quantitation for BPA and BPA-G in mouse analysis of BPA (retention time 1.52 min) and BPA-G 94, 353-355.
serum were 0.5 ng/mL and 0.2 ng/mL, respectively. Although (retention time 1.04 min) in mouse serum after receiving 13. R.R. Gerona, T.J. Woodruff, C.A. Dickenson, J. Pan, J.M.
these LLOQ values for BPA and BPA-G in serum are not the lowest dose of vegetable oil vehicle as a control (top) or in mouse Schwartz, S. Sen, M. Friesen, V.Y. Fujimoto, P.A. Hunt
in the literature, the serum sample size used in our experiments serum after administration of oil containing 10 µg/kg BPA Environ. Sci. Technol. DOI: 10.1021/es402764d 13 Aug 2013.
(25 µL) was at least 10-fold smaller than previous methods. For (bottom). 14. P.V. Karalius, J.E. Harbison, R.B. van Breemen, G. Li, K. Huang,
13
example, using UHPLC-MS-MS Gerano et al . reported an LLOQ N. Mora, L.R. Dugas, L. Vail, N.C. Tuchman, T. Forrester, J.
of 0.1 for both BPA and BPA-G in serum using a sample size of Plange-Rhule, A. Luke. Environ. Health Insights, in press.
250 µL serum. Therefore, on a sample size basis, our method is as
sensitive as any in the literature.
The method for measuring BPA in water was applied to the
analysis of drinking water and surface water samples from the
Chicago area, Jamaica and Ghana. BPA in water in these samples
ranged from none detected to up to 0.186 ng/mL. These data are
34