Page 5 - Shimadzu UV-3600 Plus
P. 5
Highest Sensitivity in Class with
Three Detectors
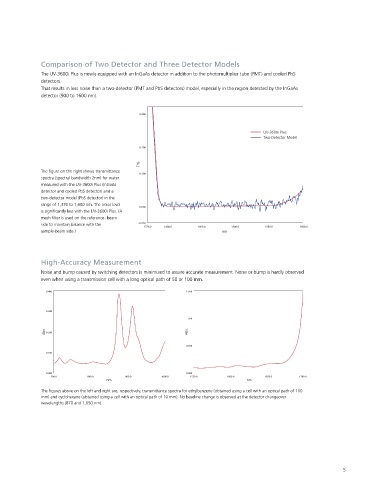
The UV-3600i Plus provides precise transmittance or reflectance measurements in the ultraviolet to near-infrared Comparison of Two Detector and Three Detector Models
regions. The level of sensitivity in the near-infrared region is significantly enhanced by using the combination of an The UV-3600i Plus is newly equipped with an InGaAs detector in addition to the photomultiplier tube (PMT) and cooled PbS
InGaAs detector and a cooled PbS detector for this region. Spectra can be obtained without interruption for the detectors.
entire range, with a high level of sensitivity and precision. That results in less noise than a two-detector (PMT and PbS detectors) model, especially in the region detected by the InGaAs
detector (900 to 1600 nm).
InGaAs
0.300
UV-3600i Plus
Two-Detector Model
PbS 0.200
T%
The figure on the right shows transmittance
PbS detector InGaAs detector 0.100
spectra (spectral bandwidth 2nm) for water
measured with the UV-3600i Plus (InGaAs
detector and cooled PbS detector) and a
PMT two-detector model (PbS detector) in the
range of 1,370 to 1,600 nm. The noise level
0.000
Optical system around detectors is significantly less with the UV-3600i Plus. (A
mesh filter is used on the reference- beam
side to maintain balance with the -0.050
1370.0 1400.0 1450.0 1500.0 1550.0 1600.0
sample-beam side.) nm
Sensitivity Characteristic
100
PMT detector
High-Accuracy Measurement
PMT
Relative Value InGaAs Conventional spectrophotometers use a PMT (photomultiplier tube) Noise and bump caused by switching detectors is minimized to assure accurate measurement. Noise or bump is hardly observed
even when using a transmission cell with a long optical path of 50 or 100 mm.
PbS
for the ultraviolet and visible region and a PbS detector for the
near-infrared region. Neither detector, however, is very sensitive
near the wavelength of 900 nm, This prevents high-sensitivity 0.400 1.500
measurements in this range. The UV-3600i Plus makes it possible to
0 take high-sensitivity measurements in the switchover range by 0.300
1000 2000 3000
incorporating an InGaAs detector as shown in the figure on the 1.00
Wavelength (nm)
left.
Abs. 0.200 Abs.
Relationship between Detectors and Measurable Range 0.500
0.100
165 nm 380 nm 780 nm 3300 nm
0.000 0.000
UV Visible NIR 700.0 800.0 900.0 1000.0 1550.0 1600.0 1650.0 1700.0
nm nm
PMT 185~1000 nm The figures above on the left and right are, respectively, transmittance spectra for ethylbenzene (obtained using a cell with an optical path of 100
mm) and cyclohexane (obtained using a cell with an optical path of 10 mm). No baseline change is observed at the detector changeover
InGaAs 700~1800 nm wavelengths (870 and 1,650 nm).
PbS 1600~3300 nm
Switching between the photomultiplier tube and the InGaAs detector is possible in the range of 700 to 1,000 nm (the default switchover
wavelength is 830 nm). Switching between the InGaAs detector and the PbS detector is possible in the range of 1,600 to 1,800 nm (the default
switchover wavelength is 1,650 nm).
4 5