Page 59 - Pharmaceutical Solution for Pharma Analysis
P. 59
3 Comparison of GC-FID and GC-MS Chromatograms
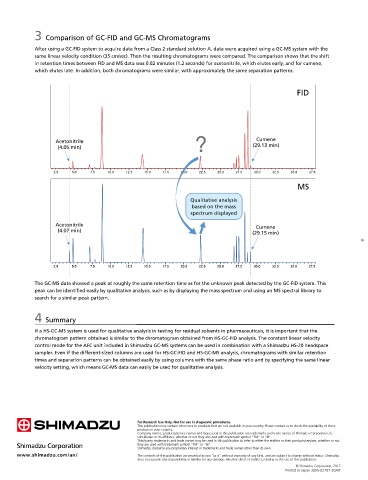
After using a GC-FID system to acquire data from a Class 2 standard solution A, data were acquired using a GC-MS system with the
same linear velocity condition (35 cm/sec). Then the resulting chromatograms were compared. The comparison shows that the shift
in retention times between FID and MS data was 0.02 minutes (1.2 seconds) for acetonitrile, which elutes early, and for cumene,
which elutes late. In addition, both chromatograms were similar, with approximately the same separation patterns.
FID
Acetonitrile Cumene
(4.05 min) (29.13 min)
MS
Qualitative analysis
based on the mass
spectrum displayed
Acetonitrile Cumene
(4.07 min) (29.15 min)
The GC-MS data showed a peak at roughly the same retention time as for the unknown peak detected by the GC-FID system. This
peak can be identified easily by qualitative analysis, such as by displaying the mass spectrum and using an MS spectral library to
search for a similar peak pattern.
4 Summary
If a HS-GC-MS system is used for qualitative analysis in testing for residual solvents in pharmaceuticals, it is important that the
chromatogram pattern obtained is similar to the chromatogram obtained from HS-GC-FID analysis. The constant linear velocity
control mode for the AFC unit included in Shimadzu GC-MS systems can be used in combination with a Shimadzu HS-20 headspace
sampler. Even if the different-sized columns are used for HS-GC-FID and HS-GC-MS analysis, chromatograms with similar retention
times and separation patterns can be obtained easily by using columns with the same phase ratio and by specifying the same linear
velocity setting, which means GC-MS data can easily be used for qualitative analysis.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
This publication may contain references to products that are not available in your country. Please contact us to check the availability of these
products in your country.
Company names, products/service names and logos used in this publication are trademarks and trade names of Shimadzu Corporation, its
subsidiaries or its affiliates, whether or not they are used with trademark symbol “TM” or “®”.
Third-party trademarks and trade names may be used in this publication to refer to either the entities or their products/services, whether or not
they are used with trademark symbol “TM” or “®”.
Shimadzu disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names other than its own.
www.shimadzu.com/an/ The contents of this publication are provided to you “as is” without warranty of any kind, and are subject to change without notice. Shimadzu
does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the use of this publication.
© Shimadzu Corporation, 2017
Printed in Japan 3655-02707-20AIT