Page 80 - Clinical-Medical Solution for Clinical Chemistry
P. 80
Application No. G286
News
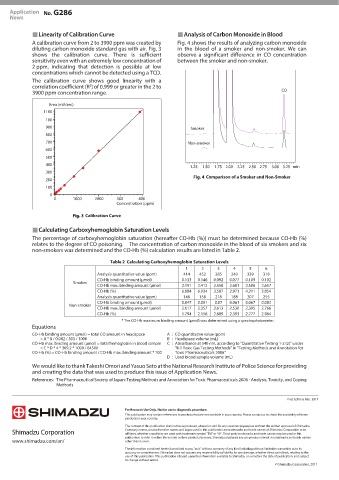
Linearity of Calibration Curve Analysis of Carbon Monoxide in Blood
A calibration curve from 2 to 3900 ppm was created by Fig. 4 shows the results of analyzing carbon monoxide
diluting carbon monoxide standard gas with air. Fig. 3 in the blood of a smoker and non-smoker. We can
shows the calibration curve. There is sufficient observe a significant difference in CO concentration
sensitivity even with an extremely low concentration of between the smoker and non-smoker.
2 ppm, indicating that detection is possible at low
concentrations which cannot be detected using a TCD.
The calibration curve shows good linearity with a
correlation coefficient (R ) of 0.999 or greater in the 2 to
2
3900 ppm concentration range. CO
Area (mV/sec)
1100
100
900 Smoker
800
700 Non-smoker
600
500
400
1.25 1.50 1.75 2.00 2.25 2.50 2.75 3.00 3.25 min
300
Comparison of a Smoker and Non-Smoker
200
100
0
0 1000 2000 300 400
Concentration (ppm)
Calibration Curve
Calculating Carboxyhemoglobin Saturation Levels
The percentage of carboxyhemoglobin saturation (hereafter CO-Hb (%)) must be determined because CO-Hb (%)
relates to the degree of CO poisoning. The concentration of carbon monoxide in the blood of six smokers and six
non-smokers was determined and the CO-Hb (%) calculation results are listed in Table 2.
Table 2 Calculating Carboxyhemoglobin Saturation Levels
1 2 3 4 5 6
Analysis quantitative value (ppm) 414 452 285 240 339 318
CO-Hb binding amount (μmol) 0.133 0.146 0.092 0.077 0.109 0.102
Smoker
CO-Hb max. binding amount (μmol) 2.191 2.412 2.558 2.601 2.586 2.657
CO-Hb (%) 6.084 6.034 3.587 2.971 4.211 3.854
Analysis quantitative value (ppm) 146 158 218 188 207 255
CO-Hb binding amount (μmol) 0.047 0.051 0.07 0.061 0.067 0.082
Non-smoker
CO-Hb max. binding amount (μmol) 2.617 2.357 2.613 2.530 2.395 2.766
CO-Hb (%) 1.794 2.156 2.689 2.393 2.777 2.964
* The CO-Hb maximum binding amount (μmol) was determined using a spectrophotometer.
Equations
CO-Hb binding amount (μmol) = total CO amount in headspace A : CO quantitative value (ppm)
= A * B / 0.082 / 303 / 1000 B : Headspace volume (mL)
CO-Hb max. binding amount (μmol) = total hemoglobin in blood sample C : Absorbance at 540 nm, according to "Quantitative Testing 1-2 (2)" under
= C * D * 4 * 369.2 * 1000 / 64500 "II-1 Toxic Gas Testing Methods" in "Testing Methods and Annotation for
CO-Hb (%) = CO-Hb binding amount / CO-Hb max. binding amount * 100 Toxic Pharmaceuticals 2006"
D : Used blood sample volume (mL)
We would like to thank Takeshi Omori and Yasuo Seto at the National Research Institute of Police Science for providing
and creating the data that was used to produce this issue of Application News.
References: The Pharmaceutical Society of Japan: Testing Methods and Annotation for Toxic Pharmaceuticals 2006 - Analysis, Toxicity, and Coping
Methods
First Edition: Mar. 2017
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedure.
This publication may contain references to products that are not available in your country. Please contact us to check the availability of these
products in your country.
The content of this publication shall not be reproduced, altered or sold for any commercial purpose without the written approval of Shimadzu.
Company names, product/service names and logos used in this publication are trademarks and trade names of Shimadzu Corporation or its
affiliates, whether or not they are used with trademark symbol “TM” or “£”. Third-party trademarks and trade names may be used in this
publication to refer to either the entities or their products/services. Shimadzu disclaims any proprietary interest in trademarks and trade names
www.shimadzu.com/an/ other than its own.
The information contained herein is provided to you "as is" without warranty of any kind including without limitation warranties as to its
accuracy or completeness. Shimadzu does not assume any responsibility or liability for any damage, whether direct or indirect, relating to the
use of this publication. This publication is based upon the information available to Shimadzu on or before the date of publication, and subject
to change without notice.
© Shimadzu Corporation, 2017