Page 8 - Automotive2-Railroad Industry
P. 8
Hardness Evaluation of Wheels and Rails
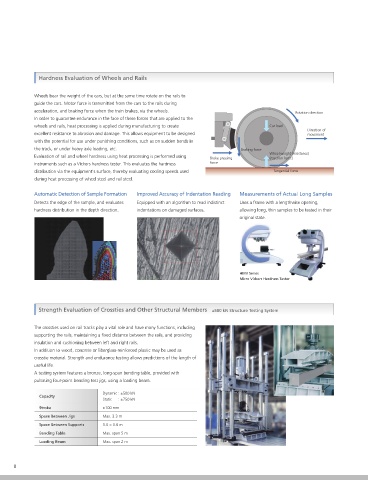
Wheels bear the weight of the cars, but at the same time rotate on the rails to
guide the cars. Motor force is transmitted from the cars to the rails during
acceleration, and braking force when the train brakes, via the wheels. Rotation direction
In order to guarantee endurance in the face of these forces that are applied to the
wheels and rails, heat processing is applied during manufacturing to create Car load
Direction of
excellent resistance to abrasion and damage. This allows equipment to be designed movement
with the potential for use under punishing conditions, such as on sudden bends in
the track, or under heavy axle loading, etc. Braking force
Wheel weight (resistance)
Evaluation of rail and wheel hardness using heat processing is performed using Brake pressing (reaction force)
instruments such as a Vickers hardness tester. This evaluates the hardness force
distribution via the equipment's surface, thereby evaluating cooling speeds used Tangential force
during heat processing of wheel steel and rail steel.
Automatic Detection of Sample Formation Improved Accuracy of Indentation Reading Measurements of Actual Long Samples
Detects the edge of the sample, and evaluates Equipped with an algorithm to read indistinct Uses a frame with a lengthwise opening,
hardness distribution in the depth direction. indentations on damaged surfaces. allowing long, thin samples to be tested in their
original state.
HMV Series
Micro Vickers Hardness Tester
Strength Evaluation of Crossties and Other Structural Members ±500 kN Structure Testing System
The crossties used on rail tracks play a vital role and have many functions, including
supporting the rails, maintaining a fixed distance between the rails, and providing
insulation and cushioning between left and right rails.
In addition to wood, concrete or fiberglass-reinforced plastic may be used as
crosstie material. Strength and endurance testing allows predictions of the length of
useful life.
A testing system features a bronze, long-span bending table, provided with
pulsating four-point bending test jigs, using a loading beam.
Dynamic : ±500 kN
Capacity
Static : ±750 kN
Stroke ±100 mm
Space Between Jigs Max. 3.3 m
Space Between Supports 1.0 × 0.6 m
Bending Table Max. span 5 m
Loading Beam Max. span 2 m
8