Page 15 - Shimadzu Nexis GC-2030
P. 15
Application Systems Tailored to For more Nexis GC-2030 applications,
visit our web page:
Your Analytical Requirements
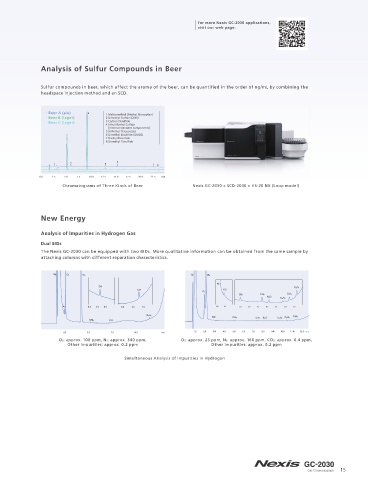
Pharmaceuticals Analysis of Sulfur Compounds in Beer
UPS 467 Sulfur compounds in beer, which affect the aroma of the beer, can be quanti ed in the order of ng/mL by combining the
Analysis of Residual Solvents in Pharmaceuticals
headspace injection method and an SCD.
A headspace sampler maintains the sample at a constant
temperature and then injects a xed quantity of the gas
phase generated into a GC unit. · Beer A (ale) 4 1 Methanethiol (Methyl Mercaptan)
It is used for qualitative and quantitative analysis of volatile · Beer B (lager) 2 Dimethyl Sulfide (DMS)
3 Carbon Disulfide
components in solid or liquid samples. The further strides in · Beer C (lager) 4 Ethyl Methyl Sulfide
[internal standard components]
performance and user-friendly design of the HS-20 series 5 S-Methyl Thioacetate
provide strong support for a wide variety of analyses, from 2 6 Dimethyl Disulfide (DMDS)
7 Diethyl Disulfide
work in research departments to quality control. Nexis GC-2030 + HS-20 NX (Loop model) 8 Dimethyl Trisulfide
Class 2A Procedure A Helium Carrier Gas Solvent: DMF Class 2A Procedure A Helium Carrier Gas Solvent: Water 6
1 3 5 7 8
0.0 2.5 5.0 7.5 10.0 12.5 15.0 17.5 20.0 22.5 min
Chromatograms of Three Kinds of Beer Nexis GC-2030 + SCD-2030 + HS-20 NX (Loop model)
New Energy
No carryover of DMF
Analysis of Impurities in Hydrogen Gas
Analysis of Trace Residual Solvents in Pharmaceuticals Using Headspace GC,
Class 2 Standard Solution Dual BIDs
The Nexis GC-2030 can be equipped with two BIDs. More qualitative information can be obtained from the same sample by
Foods attaching columns with different separation characteristics.
Analysis of Residual Pesticide in Foods
When analyzing residual pesticides in foods, it is advantageous to use a high-sensitivity selective detector. In contrast, an
FID, which is suitable for general-purpose applications, is used to comprehensively measure many different pesticides.
Using an ECD/FPD detector con guration provides high-sensitivity analysis of phosphorus, sulfur and halogen while an FID
measures a wide variety of pesticides.
1 FPD1
O 2: approx. 100 ppm, N 2: approx. 340 ppm, O 2: approx. 25 ppm, N 2: approx. 160 ppm, CO 2: approx. 0.4 ppm,
Other impurities: approx. 0.2 ppm Other impurities: approx. 0.2 ppm
Simultaneous Analysis of Impurities in Hydrogen
Analysis of Chlorinated Pesticides in Analysis of Phosphorus Pesticides in Carrots via FPD
Traditional Chinese Medicines via ECD
1 Hexachlorobenzene 5 Heptachlor-2,3-exo-epoxide 1 Omethoate 7 Chlorpyrifos-methyl 13 Bromophos-ethyl
2 Quintozene 6 Heptachlor endo-epoxide 2 Ethoprophos 8 Paraoxon 14 Profenofos
3 Heptachlor 7 trans-Chlordane(Ѝ) 3 Phorate 9 Fenitrothion 15 Ethion
4 Oxychlordane 8 cis-Chlordane(Ћ) 4 Fonofos 10 Bromophos 16 leptophos
5 Diazinon 11 Crotoxyphos 17 Pyrazophos
6 Iprobenfos 12 Disulfoton sulfone
14 Gas Chromatograph 15