Page 19 - Shimadzu Nexera X2
P. 19
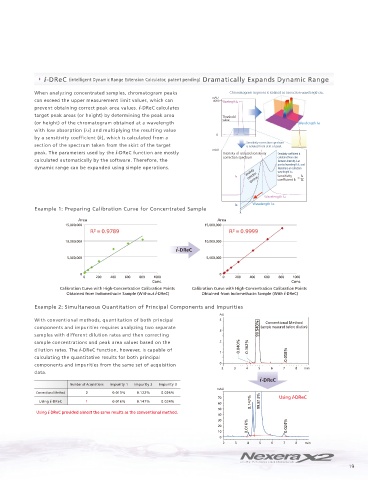
i-DReC (intelligent Dynamic Range Extension Calculator, patent pending) Dramatically Expands Dynamic Range
When analyzing concentrated samples, chromatogram peaks Chromatogram segment is isolated at correction wavelength λb.
mAU
can exceed the upper measurement limit values, which can 4000 Wavelength λa
prevent obtaining correct peak area values. i-DReC calculates
target peak areas (or height) by determining the peak area Threshold
value
(or height) of the chromatogram obtained at a wavelength Wavelength λb
with low absorption (λb) and multiplying the resulting value
0
by a sensitivity coefficient (k), which is calculated from a
Sensitivity correction spectrum
section of the spectrum taken from the skirt of the target is isolated from skirt of peak.
mAU
peak. The parameters used by the i-DReC function are mostly Intensity of isolated sensitivity Sensitivity coefficient is
correction spectrum calculated from ratio
calculated automatically by the software. Therefore, the between intensity Ia at
spectral wavelength λa and
dynamic range can be expanded using simple operations. intensity Ib at correction
Sensitivity wavelength λb.
Ia correction Sensitivity = Ia Ib
spectrum
coefficient k
Wavelength λa
Wavelength λb
Ib
Example 1: Preparing Calibration Curve for Concentrated Sample
λ
Area Area
15,000,000 15,000,000
10,000,000 10,000,000
i -DReC
5,000,000 5,000,000
0 0
0 200 400 600 800 1000 0 200 400 600 800 1000
Conc. Conc.
Calibration Curve with High-Concentration Calibration Points Calibration Curve with High-Concentration Calibration Points
Obtained from Indomethacin Sample (Without i-DReC) Obtained from Indomethacin Sample (With i-DReC)
Example 2: Simultaneous Quantitation of Principal Components and Impurities
AU
With conventional methods, quantitation of both principal 4 Conventional Method
components and impurities requires analyzing two separate (sample measured before dilution)
3 99.540%
samples with different dilution rates and then correcting
sample concentrations and peak area values based on the 2
dilution rates. The i-DReC function, however, is capable of 0.040% 0.362%
1
calculating the quantitative results for both principal 0.058%
components and impurities from the same set of acquisition 0
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 min
data.
i -DReC
Number of Acquisitions Impurity 1 Impurity 2 Impurity 3
mAU
Conventional Method 2 0.013% 0.122% 0.026%
70 Using i-DReC
Using i-DReC 1 0.016% 0.147% 0.024% 0.147% 99.813%
60
50
Using i-DReC provided almost the same results as the conventional method.
40
30
20 0.016% 0.024%
10
0
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 min
19